Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
- Assessment Limits :
Items may only contain whole numbers from 0 to 1,000. Operations in rules are limited to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Items may not contain a rule that exceeds two procedural operations. Division rules may not require fractional responses. Rules may not be provided algebraically (e.g., x + 5). Items must provide the rule. - Calculator :
No
- Context :
Allowable
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
The first number in a pattern is 5. The pattern follows the rule "Add 3."
What is the next number in the pattern?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
A pattern starts with one triangle and follows the rule: "Add one triangle to the top, add one triangle to the left, add one triangle to the right."
The first three figures for the pattern are shown.
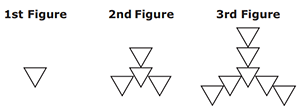
Complete the statement to describe the 4th figure for the pattern shown. For each blank, fill in the circle before the word or phrase that is correct.
The 4th figure for the pattern will have an

number of triangles because
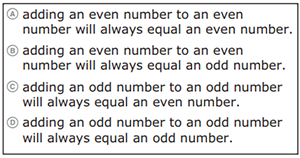
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: ETC: Editing Task Choice
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Educational Game
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorial
Perspectives Video: Teaching Idea
Problem-Solving Task
Teaching Ideas
Tutorial
Virtual Manipulative
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
Students will work in groups to assist a client in purchasing different fish for a fish pond. From a data table, they will need to decide which type of fish and how many fish to purchase according to the size of the each pond. After, they will need to revisit a revised data table to make different selection of fish and calculate costs for the purchase of the fish.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students generate a number pattern based on a given rule and explain the pattern found.
Students are asked to generate a sequence of numbers based on a given rule and then to identify features of the pattern that are not explicit.
Students are asked to analyze a shape pattern, continue the pattern, and identify what a future shape will be if the pattern continues.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades K-5
Join Pete as he explores patterns within patterns with feisty Wubbles and Dipples in this interactive tutorial.
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
Join Pete as he explores patterns within patterns with feisty Wubbles and Dipples in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to help students gain a better understanding of patterns. This task is meant to be used in an instructional setting.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Tutorial
In this Khan Academy tutorial video a table is used to track a growing sequence of design.
Type: Tutorial
Virtual Manipulative
Students select the shape that goes next in the pattern and place it in the row, then identify the overall pattern.
Type: Virtual Manipulative
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to help students gain a better understanding of patterns. This task is meant to be used in an instructional setting.
Type: Problem-Solving Task