Remarks
Example: Suppose a building is in the shape of a regular hexagon. The architect wants to put walkways as indicated. Show that the triangles formed are equal in size and shape.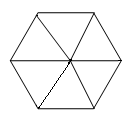
-
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
,
FR
item(s)
Also Assesses: - Clarification :
Students will use properties of congruent and/or similar polygons to solve problems. - Content Limits :
All angle measurements will be in degrees.
Items may require statements and/or justifications to complete formal and informal proofs.
- Stimulus Attributes :
Graphics should be used in these items, as appropriate.
MA.912.G.2.1 Identify and describe convex, concave, regular, and irregular polygons.
MA.912.G.4.1 Classify, construct, and describe triangles that are right, acute, obtuse, scalene, isosceles, equilateral, and equiangular.
MA.912.G.4.2 Define, identify, and construct altitudes, medians, angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors, orthocenter, centroid, incenter, and circumcenter.
MA.912.G.4.4 Use properties of congruent and similar triangles to solve problems involving lengths and areas.
MA.912.G.4.5 Apply theorems involving segments divided proportionally.
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
The owners of a water park want to build a scaled-down version of a popular tubular water slide for the children’s section of the park. The side view of the water slide, labeled ABC, is shown below.
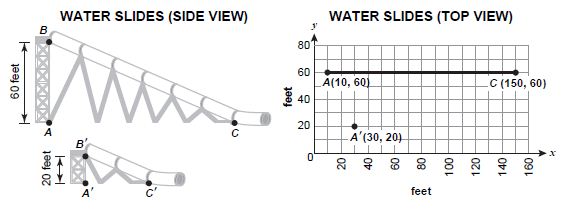
Points A', B' and C ', shown above, are the corresponding points of the scaled-down slide. Which of the following would be closest to the coordinates of a new point C ' that will make slide A'B'C ' similar to slide ABC ?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
Malik runs on the trails in the park. He normally runs 1 complete lap around trail ABCD. The length of each side of trail ABCD is shown in meters (m) in the diagram below.
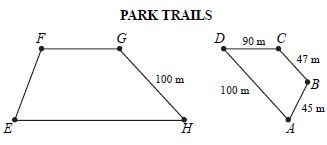
If trail EFGH is similar in shape to trail ABCD, what is the minimum distance, to the nearest whole meter, Malik would have to run to complete one lap around trail EFGH ?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: FR: Fill-in Response




