Know and justify that when adding a rational number and an irrational number the result is irrational.
Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Recognize rational numbers (numbers you can write as a fraction).
- Recognize irrational numbers (approximations like square root of 2, or pi).
- Identify the patterns in adding irrational numbers by rational numbers.
- Understand rational number – any number you can write as a fraction.
- Understand irrational number – non-repeating, non-terminating decimal number (various square roots, pi).
- The sum of a rational number and an irrational number is an irrational number
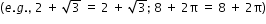 .
.
General Information
Number: MAFS.912.N-RN.2.AP.3b
Category: Access Points
Date Adopted or Revised:
07/14
Cluster:
Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. (Algebra 1 - Additional Cluster) :
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Related Standards
This access point is an alternate version of the following benchmark(s).
Related Courses
This access point is part of these courses.
1200310: Algebra 1
1200320: Algebra 1 Honors
1200380: Algebra 1-B
1200400: Foundational Skills in Mathematics 9-12
1207310: Liberal Arts Mathematics
1200300: Basic Mathematics Skills (Formerly Pre-Algebra)
1206330: Analytic Geometry
1200700: Mathematics for College Algebra
7912090: Access Algebra 1B
1200315: Algebra 1 for Credit Recovery
1200385: Algebra 1-B for Credit Recovery
7912100: Fundamental Algebraic Skills
7912075: Access Algebra 1
Related Resources
Vetted resources educators can use to teach the concepts and skills in this access point.
Student Resources
Vetted resources students can use to learn the concepts and skills in this access point.
Parent Resources
Vetted resources caregivers can use to help students learn the concepts and skills in this access point.