Remarks
Example 1: You ride your bike from your house to the beach and home again. At the end of your trip, your bicycle odometer reads 8km. How many miles did you ride?Example 2: How many cm3 are in a 2-liter bottle of soda?
-
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
,
GR
item(s)
At Grade 7, this benchmark will be assessed using MC and GR items.
- Clarification :
Students will compare, contrast, and convert:
- linear units of measure between different measurement systems (US customary or metric [SI]);
- derived units with respect to linear measurement within the same system; and
- linear units of measure within the same system to solve real-world problems.
- Content Limits :
Items may include conversions from customary to metric or vice versa, using only one of the conversions found on the reference sheet.
Items may include up to three conversions within the same system of measurement (e.g., millimeters to centimeters, centimeters to meters, and meters to kilometers).
Items may include conversions within the same unit of measure when converting derived units (e.g., miles per hour to feet per second).
Items may include converting a denominate number (e.g., 5 ft 3 in.) to a single unit within the same system of measurement, or vice versa.
Gridded-response items may only involve conversions within the same system of measurement.
Items will not include a combination of multiple conversions within the same system and across different measurement systems (e.g., convert meters to inches). - Stimulus Attributes :
All items should be set in a real-world context.
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question: Rebecca bought a rectangular throw blanket like the one shown below.
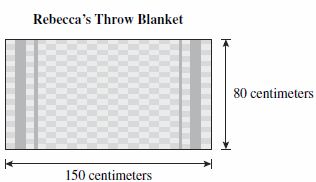
Which is closest to the dimensions of Rebecca’s throw blanket?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question: Clarissa has a lamp that measures 6 1/2 feet in height. What is the height, in inches, of the lamp?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: GR: Gridded-Response
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Lesson Plan
Problem-Solving Task
Teaching Idea
Tutorial
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
Students will be helping Lily Rae find the most efficient delivery route by using speed and distance values to calculate the shortest time to make it to all of her customers.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
Student Resources
Tutorial
In this lesson, students will be viewing a Khan Academy video that will show how to convert ratios using speed units.
Type: Tutorial







