Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric figures, and apply these relationships to solve problems.
Remarks
See Example 2 in benchmark MA.7.A.1.6. The linear scale factor is 2. The areas of the two figures are related by a factor of 4 (2 squared). If this pattern was continued for a 3-dimensional figure, the volumes would be related by a factor of 8 (2 cubed). Students should encounter this concept in different contexts, and they should be encouraged to recognize the patterns themselves rather than be told about the relationship first.
Example: You have two circles with circumference pi and 4pi. What is the ratio of the areas of the circles? What is the ratio of the diameters? What is the ratio of the radii?
General Information
Subject Area: X-Mathematics (former standards - 2008)
Grade: 7
Body of Knowledge: Geometry
Idea: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
Supporting Idea: Geometry and Measurement - Geometry and Measurement
Date Adopted or Revised: 09/07
Content Complexity Rating:
Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
-
More Information
Date of Last Rating: 06/07
Status: State Board Approved - Archived
Assessed: Yes
Test Item Specifications
-
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
,
GR
item(s)
At Grade 7, this benchmark will be assessed using MC and GR items.
- Clarification :
Students will determine the effects of changing dimensions on perimeter, circumference, area, and volume.
Students will solve problems involving the effects of changing dimensions on perimeter, circumference, area, and volume. - Content Limits :
Items that increase the dimensions of a figure should use scale factors that are whole numbers less than or equal to 25.
Items that decrease the dimensions of a figure should use scale factors of 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/10, 10%, 20%, 25%, or 50%. Distractors in MC items may exceed this limit.
Items assessing change in volume should only include right-rectangular prisms and right-circular cylinders.
Items will not assess changes in surface area. - Stimulus Attributes :
Items should be set in a real-world or mathematical context.
Items that are set in real-world context may use length and width as dimensions as well as base and height as dimensions.
Graphics should be used in most of these items, as appropriate.
Sample Test Items (2)
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question: Toni has a rectangular vegetable garden that measures 12 feet by 18 feet. She wants to reduce the area of her garden. If Toni reduces the dimensions of her garden to 12 feet by 9 feet, how will the area of the new garden compare to the area of the old garden?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
Jeff is building walls using the building blocks shown below. The dimensions of the small blocks are 1/2 the size of the dimensions of the large blocks. Jeff’s wall has a length (l) of 5 large blocks and a height (h) of 2 large blocks.
Building Blocks
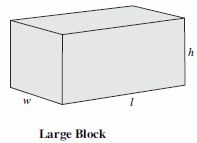
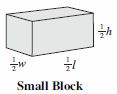
How many small blocks does Jeff need to build a wall with the same volume as the wall he made with large blocks? - Difficulty: N/A
- Type: GR: Gridded-Response
Related Access Points
Alternate version of this benchmark for students with significant cognitive disabilities.
Related Resources
Vetted resources educators can use to teach the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Virtual Manipulative
Student Resources
Vetted resources students can use to learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Virtual Manipulative
Scale Factor:
Explore the effect on perimeter and area of two rectangular shapes as the scale factor changes.
Type: Virtual Manipulative
Parent Resources
Vetted resources caregivers can use to help students learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.







