Remarks
Physical objects, drawings, and dynamic geometry software might help students explore this benchmark. Students' early work in elementary and middle school should form a base for teaching this benchmark (see MA.3.G.3.3, MA.4.G.5.2, and MA.7.G.4.2). Students should explore different types of transformations and observe that some transformations (translations, reflections, and rotations) result in congruent shapes.
Example: Explore regular polygons through manipulatives and/or drawing programs. Describe which of the polygons would be best for tiling a rectangular floor. Explain your reasoning.
-
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
,
FR
item(s)
- Clarification :
Students will apply transformations to polygons to determine congruence, similarity, and symmetry. - Content Limits :
Items may include using coordinate geometry to perform transformations in the plane.
Items may require statements and/or justifications to determine congruence, similarity, and symmetry.
- Stimulus Attributes :
Items may assess transformations, including translations, reflections, rotations, dilations, and scale factors.
Graphics should be used for most of these items, as appropriate.
Items may be set in either real-world or mathematical contexts.
- Response Attributes :
Fill-in response items may require that students provide the length of a segment or the x-coordinate (or y-coordinate) of a point of interest.
Fill-in response items may have a negative answer. 64
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
A top view of downtown Rockford is shown on the grid below, with Granite Park represented by quadrilateral ABCD. The shape of a new park, Mica Park, will be similar to the shape of Granite Park. Vertices L and M will be plotted on the grid to form quadrilateral JKLM, representing Mica Park.
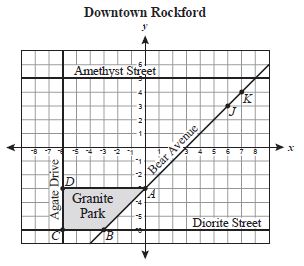
Which of the following coordinates for L and M could be vertices of JKLM so that the shape of Mica Park is similar to the shape of Granite Park?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
Pentagon ABCDE is shown below on a coordinate grid. The coordinates of A, B, C, D, and E all have integer values.
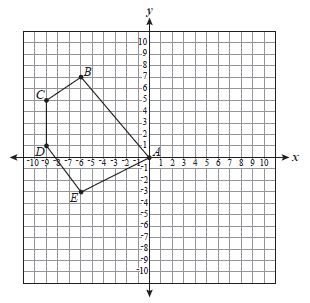
If pentagon ABCDE is rotated 90º clockwise about point A to create pentagon A'B'C'D'E', what will be the x-coordinate of E'?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: FR: Fill-in Response





