MA.912.GR.4.6
Alternate version of this benchmark for students with significant cognitive disabilities.
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Circle
- Cone
- Cylinder
- Prism
- Pyramid
- Rectangle
- Sphere
- Square
- Triangle
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In middle grades, students determined surface area using nets and formulas for right rectangular prisms, right rectangular pyramids and right circular cylinders. In Geometry, students explore for the first time the surface area of cones and spheres. Instruction includes reviewing units and conversions within and across different measurement systems (as this was done in middle grades).- Instruction includes discussing the convenience of answering with exact values (e.g., the simplest radical form or in terms of pi) or with approximations (e.g., rounding to the 22 nearest tenth or hundredth or using 3.14, or other approximations for pi). It is also important to explore the consequences of rounding partial answers on the accuracy or precision of the final answer, especially when working in real-world contexts.
- Instruction includes reviewing the definition of cylinders, pyramids, prisms, cones and spheres (as this was done in grade 5), and discussing the definitions of right and oblique polyhedrons, cubes, tetrahedrons, regular prisms and regular pyramids.
- Instruction includes the connection to finding areas of two-dimensional figures to
determine the surface area of cylinders, pyramids, prisms and cones.
- For example, the surface area of a cylinder is the result of combining the area of the bases (circles with radius ) with the lateral area (a rectangle with base = 2π and height equal to the height of the cylinder). The area of the circles is π2 and the area of the rectangle is which is equivalent to which is equivalent to 2 π. Therefore, given a cylinder with radius and height , its surface area is 2π2 + 2π
- For example, the surface area of a cone is the result of combining the area of the
base (a circle with radius and circumference ) and the area of the curved
surface (a circular sector with radius , which is the slant height of the cone
and arc length ). The slant height is
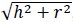 , where is the height of the
cone. The area of the circle is π2 and the area of the circular sector is
(arc length)(radius), which is equivalent to , which is equivalent to (2π), which is equivalent to πrL. Therefore, given a cone with radius and height , its surface area if π2 + π = π2 + π
, where is the height of the
cone. The area of the circle is π2 and the area of the circular sector is
(arc length)(radius), which is equivalent to , which is equivalent to (2π), which is equivalent to πrL. Therefore, given a cone with radius and height , its surface area if π2 + π = π2 + π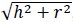 is π( +
is π( + 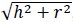 ).
).
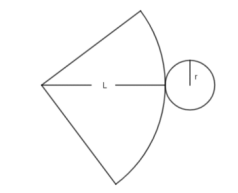
- Instruction includes exploring the surface area of cylinders, pyramids and prisms as the result of combining areas of triangles, rectangles and circles (and when needed, other polygons). Students should understand the similarities and differences between lateral area and surface area. (MTR.2.1)
- Since deriving the surface area of a sphere requires Calculus, students will not be able to explore its formula and can be calculated using the formula = 4π2.
- Instruction includes exploring a variety of real-world situations where finding the surface area is relevant for different purposes. Problem types include components like percentages, cost and budget, constraints, comparisons, or others.
- Problem types include finding missing dimensions given the surface area of a three-dimensional figure, finding the surface area of composite figures or determining which face to include in calculations within real-world context (i.e., the surface area required to paint a house, the surface area that will be covered by a label in a soup can).
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may have trouble working with formulas by making incorrect substitutions or incorrect use of the order of operations.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.7.1)- There are three Pyramids of Giza. The largest, the Great Pyramid, has an approximately square base with side lengths averaging 230 meters and a lateral surface area of 85,836 square meters. What is the height of the Great Pyramid?

Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1)
- The surface area of a sphere with radius 10 is 400π square units.
- Part A. Discuss the value of this kind of answer for its accuracy and precision.
- Part B. Discuss the effect of replacing π in the formulas with 3.14, 3.1416, and other approximations. What happens with the answer, the surface area of the figure, in each case?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- Kristin and Rachel are hosting an art show where they will showcase local artists’ sculptures. They are painting pedestals upon which the sculptures will be placed. Pictures of the pedestals they will be using are below. One gallon of paint can cover 400 square feet.
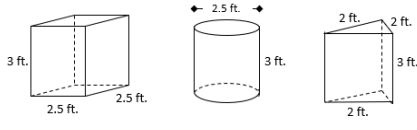
- Part A. How many gallons of paint will they need to purchase to cover at least 4 of each type of pedestal? Assume that the base of each will not be painted.
- Part B. If there is any paint left over, determine how many of which shape pedestals could be painted.
General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 912
Strand: Geometric Reasoning
Standard: Use geometric measurement and dimensions to solve problems.
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
This benchmark is part of these courses.
