General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
- translating between percents
- decimals and fractions
- representing percent increase and decrease as multiplication
- recognizing the relationship between increases and decreases
- Translating between percents, decimals, and fractions.
- Representing percent increase and decrease as multiplication.
- Recognizing the relationship between increases and decreases.
7.NS.1.2a, 2b, and 2c require the incorporation of a negative value.
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (6)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Joe and Scott equally share a pizza. If Scott eats |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 2 | In Homestead, What fraction of the households in Homestead own cats? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 3 | Sandy uses Yesterday, Sandy used |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 4 | Springfield has an elevation of −150 feet. Greenville is 3 times as far below sea level
as Springfield. What is Greenville’s elevation, in feet? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 5 | An equation is shown, where z < 0. x · y = z A. Assume x > 0. Drag the point to the number line to identify a possible location for y. B. Assume x < 0. Drag the point to the number line to identify a possible location for y.
|
N/A | GRID: Graphic Response Item Display |
| Sample Item 6 | What is
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1205020: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 6 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205040: | M/J Grade 7 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200410: | Mathematics for College Success (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022 (course terminated)) |
| 1200700: | Mathematics for College Algebra (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022 (course terminated)) |
| 7812020: | Access M/J Grade 7 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912115: | Fundamental Explorations in Mathematics 2 (Specifically in versions: 2013 - 2015, 2015 - 2017 (course terminated)) |
Related Resources
Educational Game
| Name | Description |
| Integers Jeopardy Game | This interactive game has 4 categories: adding integers, subtracting integers, multiplying integers, and dividing integers. Students can play individually or in teams. |
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Find Decimal Using Long Division | Students are asked to use long division to convert four different fractions to equivalent decimals and to identify those that are rational. |
| Understanding Products | Students are asked to explain why the product of a positive and a negative rational number is negative. |
| Negatives Explained | Students are asked to describe a real-world context for a given expression involving the product of two rational numbers. |
| Negative Times | Students are shown a problem that illustrates why the product of two negatives is a positive and are asked to provide a rationale. |
| Applying Rational Number Properties | Students are asked to evaluate expressions involving multiplication of rational numbers and use the properties of operations to simplify calculations. |
| Integer Division | Students are asked to describe a real-world context for a given expression involving the quotient of two rational integers. |
| Quotients of Integers | Students are given an integer division problem and asked to identify fractions which are equivalent to the division problem. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Radioactive Dating Lesson 4 - Recursive Division | This lesson introduces students to the idea of recursive division and its application to radioactive dating with a worksheet and Scratch programming. This is the final lesson in the Radioactive Dating Unit. |
| Independent Compound Probability | During this lesson, students will use Punnett Squares to determine the probability of an offspring's characteristics. |
| Increasing and Decreasing Quantities by a Percent | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to interpret percent increase and decrease, and in particular, to identify and help students who have the following difficulties: |
| Let's Understand Multiplication of Positive and Negative Numbers | This lesson provides teachers with a way to show students why a negative times a negative equals a positive. The lesson starts with a review of decomposition, the distributive property, and finding missing addends. Then with teacher guidance, groups of students apply these skills in a systematic way to apply properties of operations to discover the rules governing the signs of products for positive and negative factors and to multiply positive and negative numbers in mathematical and real-world problems. Finally, students independently show demonstrate mastery of the lesson objectives by completing an independent practice assessment. |
| Increasing and Decreasing Quantities by a Percent | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are
able to interpret percent increase and decrease, and in particular, to
identify and help students who have the following difficulties:
|
| Predicting the decimal equivalent for a fraction - terminating or repeating? | This lesson encourages students to make an important discovery. Will a given fraction yield a terminating or repeating decimal? Discussion includes why knowing this is important. The lesson is structured to allow exploration, discovery, and summarization. |
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Why Does a Negative Times a Negative Equal a Positive? | Use mathematical properties to explain why a negative factor times a negative factor equals a positive product instead of just quoting a rule with this interactive tutorial. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Equivalent fractions approach to non-repeating decimals | The purpose of the task is to get students to reflect on the definition of decimals as fractions (or sums of fractions), at a time when they are seeing them primarily as an extension of the base-ten number system and may have lost contact with the basic fraction meaning. Students also have their understanding of equivalent fractions and factors reinforced. |
| Repeating Decimal as Approximation | The student is asked to complete a long division which results in a repeating decimal, and then use multiplication to "check" their answer. The purpose of the task is to have students reflect on the meaning of repeating decimal representation through approximation. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Thinking About the Sign of Expressions | This video shows some examples that test your understanding of what happens when positive and negative numbers are multiplied and divided. |
| Converting repeating decimals to fractions | Students will learn how to convert difficult repeating decimals to fractions. |
| Converting repeating decimals to fractions | This tutorial shows students how to convert basic repeating decimals to fractions. |
| Converting a fraction to a repeating decimal | Students will learn how to convert a fraction into a repeating decimal. Students should know how to use long division before starting this tutorial. |
| Changing a Fraction to Decimal Form | In this video, you will practice changing a fraction into decimal form. |
| Multiplying and Dividing Even and Odd Numbers of Negatives | You will learn how multiplication and division problems give us a positive or negative answer depending on whether there are an even or odd number of negative integers used in the problem. |
| Simplifying Expressions with Rational Numbers | In this tutorial, you will simplify expressions involving positive and negative fractions. |
| Making Sense of Complex Fractions | In this tutorial, you will see how to simplify complex fractions. |
| Negative Signs in Numerators and Denominators | In this tutorial, you will evaluate fractions involving negative numbers and variables to determine if expressions are equivalent. |
| Dividing Negative Fractions | In this tutorial, you will see how to divide fractions involving negative integers. |
| Multiplying Negative and Positive Fractions | In this tutorial you will practice multiplying and dividing fractions involving negative numbers. |
| Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers | In this tutorial, you will learn rules for multiplying positive and negative integers. |
| Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers | In this tutorial you will learn how to divide with negative integers. |
| Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes a Positive | In this tutorial you will use the repeated addition model of multiplication to help you understand why multiplying negative numbers results in a positive answer. |
| Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive | In this tutorial, you will use the distributive property to understand why the product of two negative numbers is positive. |
| Pre-Algebra - Fractions and Rational Numbers | The first fractions used by ancient civilizations were "unit fractions." Later, numerators other than one were added, creating "vulgar fractions" which became our modern fractions. Together, fractions and integers form the "rational numbers." |
| Pre-Algebra - Multiplying Negative Numbers | When number systems were expanded to include negative numbers, rules had to be formulated so that multiplication would be consistent regardless of the sign of the operands. |
| Multiplying Fractions | The video describes how to multiply fractions and state the answer in lowest terms. |
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Converting Fractions to Decimal Numbers | Any fraction can be converted into an equivalent decimal number with a sequence of digits after the decimal point, which either repeats or terminates. The reason can be understood by close examination of the number line. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Why Does a Negative Times a Negative Equal a Positive?: | Use mathematical properties to explain why a negative factor times a negative factor equals a positive product instead of just quoting a rule with this interactive tutorial. |
Educational Game
| Name | Description |
| Integers Jeopardy Game: | This interactive game has 4 categories: adding integers, subtracting integers, multiplying integers, and dividing integers. Students can play individually or in teams. |
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| Repeating Decimal as Approximation: | The student is asked to complete a long division which results in a repeating decimal, and then use multiplication to "check" their answer. The purpose of the task is to have students reflect on the meaning of repeating decimal representation through approximation. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Thinking About the Sign of Expressions: | This video shows some examples that test your understanding of what happens when positive and negative numbers are multiplied and divided. |
| Converting repeating decimals to fractions : | Students will learn how to convert difficult repeating decimals to fractions. |
| Converting repeating decimals to fractions : | This tutorial shows students how to convert basic repeating decimals to fractions. |
| Converting a fraction to a repeating decimal: | Students will learn how to convert a fraction into a repeating decimal. Students should know how to use long division before starting this tutorial. |
| Changing a Fraction to Decimal Form: | In this video, you will practice changing a fraction into decimal form. |
| Multiplying and Dividing Even and Odd Numbers of Negatives: | You will learn how multiplication and division problems give us a positive or negative answer depending on whether there are an even or odd number of negative integers used in the problem. |
| Simplifying Expressions with Rational Numbers: | In this tutorial, you will simplify expressions involving positive and negative fractions. |
| Making Sense of Complex Fractions: | In this tutorial, you will see how to simplify complex fractions. |
| Negative Signs in Numerators and Denominators: | In this tutorial, you will evaluate fractions involving negative numbers and variables to determine if expressions are equivalent. |
| Dividing Negative Fractions: | In this tutorial, you will see how to divide fractions involving negative integers. |
| Multiplying Negative and Positive Fractions: | In this tutorial you will practice multiplying and dividing fractions involving negative numbers. |
| Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers: | In this tutorial, you will learn rules for multiplying positive and negative integers. |
| Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers: | In this tutorial you will learn how to divide with negative integers. |
| Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes a Positive: | In this tutorial you will use the repeated addition model of multiplication to help you understand why multiplying negative numbers results in a positive answer. |
| Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive: | In this tutorial, you will use the distributive property to understand why the product of two negative numbers is positive. |
| Pre-Algebra - Fractions and Rational Numbers: | The first fractions used by ancient civilizations were "unit fractions." Later, numerators other than one were added, creating "vulgar fractions" which became our modern fractions. Together, fractions and integers form the "rational numbers." |
| Pre-Algebra - Multiplying Negative Numbers: | When number systems were expanded to include negative numbers, rules had to be formulated so that multiplication would be consistent regardless of the sign of the operands. |
| Multiplying Fractions: | The video describes how to multiply fractions and state the answer in lowest terms. |
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Converting Fractions to Decimal Numbers: | Any fraction can be converted into an equivalent decimal number with a sequence of digits after the decimal point, which either repeats or terminates. The reason can be understood by close examination of the number line. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| Repeating Decimal as Approximation: | The student is asked to complete a long division which results in a repeating decimal, and then use multiplication to "check" their answer. The purpose of the task is to have students reflect on the meaning of repeating decimal representation through approximation. |
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Multiplying Fractions: | The video describes how to multiply fractions and state the answer in lowest terms. |

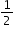 of his portion of the pizza, what fraction of the whole pizza does he eat?
of his portion of the pizza, what fraction of the whole pizza does he eat?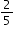 of the households own pets. Of the households with pets,
of the households own pets. Of the households with pets, 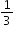 have cats.
have cats. 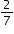 of a pound of raisins in each batch of raisin bread.
of a pound of raisins in each batch of raisin bread.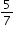 of a pound of raisins. How many batches of raisin bread did sandy make yesterday?
of a pound of raisins. How many batches of raisin bread did sandy make yesterday?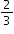 written as a decimal?
written as a decimal?