General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Items may assess relationships between vertical angles, special angles
formed by parallel lines and transversals, angle bisectors, congruent
supplements, congruent complements, and a perpendicular bisector
of a line segment.
Items may have multiple sets of lines and angles.
Items may include narrative proofs, flow-chart proofs, two-column
proofs, or informal proofs.
In items that require the student to justify, the student should not be
required to recall from memory the formal name of a theorem.
Neutral
Students will prove theorems about lines.
Students will prove theorems about angles.
Students will use theorems about lines to solve problems.
Students will use theorems about angles to solve problems.
Items may be set in a real-world or mathematical context.
Items may require the student to give statements and/or
justifications to complete formal and informal proofs.
Items may require the student to justify a conclusion from a
construction.
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
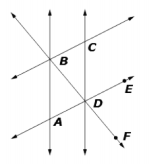
| Sample Item 1 | In the figure,
Click on the blank to enter the degree measure that completes the equation shown.
|
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 2 | 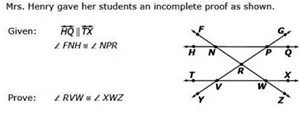 Complete the proof by dragging the correct reasons to the table for line 3 and 6. |
N/A | DDHT: Drag-and-Drop Hot Text |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1200400: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 9-12 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1206310: | Geometry (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1206320: | Geometry Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1206315: | Geometry for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912065: | Access Geometry (Specifically in versions: 2015 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Proving the Corresponding Angles Theorem | Students are asked to prove that corresponding angles formed by the intersection of two parallel lines and a transversal are congruent. |
| Name That Triangle | Students are asked to describe a triangle whose vertices are the endpoints of a segment and a point on the perpendicular bisector of a segment. |
| Finding Angle Measures - 1 | Students are asked to find the measures of angles formed by three concurrent lines and to justify their answers. |
| Finding Angle Measures - 4 | Students are asked to find the measure of an angle in a diagram containing two parallel lines and two transversals. |
| Finding Angle Measures - 3 | Students are asked to find the measures of angles formed by two parallel lines and two transversals. |
| Finding Angle Measures - 2 | Students are asked to find the measures of angles formed by two parallel lines and a transversal. |
| Proving the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem | In a diagram involving two parallel lines and a transversal, students are asked to use rigid motion to prove that alternate interior angles are congruent. |
| Equidistant Points | Students are asked to prove that a point on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. |
| Proving the Vertical Angles Theorem | Students are asked to identify a pair of vertical angles in a diagram and then prove that they are congruent. |
Image/Photograph
| Name | Description |
| Angles (Clipart ETC) | This large collection of clipart contains images of angles that can be freely used in lesson plans, worksheets, and presentations. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Engineering Design Challenge: Exploring Structures in High School Geometry | Students explore ideas on how civil engineers use triangles when constructing bridges. Students will apply knowledge of congruent triangles to build and test their own bridges for stability. |
| Parallel Thinking Debate | Students prove theorems related to parallel lines using vertical, corresponding, and alternate interior angles. |
| Vertical Angles: Proof and Problem-Solving | Students will explore the relationship between vertical angles and prove the Vertical Angle Theorem. They will use vertical angle relationships to calculate other angle measurements. |
| Proving and Using Congruence with Corresponding Angles | Students, will prove that corresponding angles are congruent. Directions for using GeoGebra software to discover this relationship is provided. |
| Determination of the Optimal Point | Students will use dynamic geometry software to determine the optimal location for a facility under a variety of scenarios. The experiments will suggest a relation between the optimal point and a common concept in geometry; in some cases, there will be a connection to a statistical concept. Algebra can be used to verify some of the conjectures. |
| Parallel Lines | Students will prove that alternate interior angles and corresponding angles are congruent given two parallel lines and a traversal. Students will use GeoGebra to explore real-world images to prove their line segments are parallel. |
| Location, Location, Location, Location? | Students will use their knowledge of graphing concurrent segments in triangles to locate and identify which points of concurrency are associated by location with cities and counties within the Texas Triangle Mega-region. |
| Accurately Acquired Angles | Students will start the lesson by playing a game to review angle pairs formed by two lines cut by a transversal. Once students are comfortable with the angle pairs the teacher will review the relationships that are created once the pair of lines become parallel. The teacher will give an example of a proof using the angle pairs formed by two parallel lines cut by a transversal. The students are then challenged to prove their own theorem in groups of four. The class will then participate in a Stay and Stray to view the other group's proofs. The lesson is wrapped up through white board questions answered within groups and then as a whole class. |
| Determination of the Optimal Point | Students will use dynamic geometry software to determine the optimal location for a facility under a variety of scenarios. The experiments will suggest a relation between the optimal point and a common concept in geometry; in some cases, there will be a connection to a statistical concept. Algebra can be used to verify some of the conjectures. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Points equidistant from two points in the plane | This task asks students to show how certain points on a plane are equidistant to points on a segment when placed on a perpendicular bisector. |
| Tangent Lines and the Radius of a Circle | This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Parallel lines and transversals | In this tutorial, students will find the measures of angles formed when a transversal cuts two parallel lines. |
| Parallel lines, transversals and triangles | This tutorial shows students the eight angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. There is also a review of triangles in this video.
|
| Parallel lines and transversal lines | Students will see in this tutorial the eight angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. |
| Parallel lines and transversals | In this tutorial, students will learn the angle measures when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. |
| Sum of Exterior Angles of an Irregular Pentagon | In this video, students will learn how to use what they know about the sum of angles in a triangle to determine the sum of the exterior angles of an irregular pentagon. |
| Proving vertical angles are equal | In this tutorial, students prove that vertical angles are equal. Students should have an understanding of supplementary angles before viewing this video. |
| Finding the measure of vertical angles | Students will use algebra to find the measure of vertical angles, or angles opposite each other when two lines cross. Students should have an understanding of complementary and supplementary angles before viewing this video. |
| Introduction to vertical angles | In this tutorial, students will use their knowledge of supplementary, adjacent, and vertical angles to solve problems involving the intersection of two lines. |
| Using Algebra to Find Measures of Angles Formed from Transversal | We will use algebra in order to find the measure of angles formed by a transversal. |
| Figuring Out Angles Between Transversal and Parallel Lines | We will be able to identify corresponding angles of parallel lines. |
| Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals | We will gain an understanding of how angles formed by transversals compare to each other. |
| Proof: Vertical Angles are Equal | This 5 minute video gives the proof that vertical angles are equal. |
Student Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Points equidistant from two points in the plane: | This task asks students to show how certain points on a plane are equidistant to points on a segment when placed on a perpendicular bisector. |
| Tangent Lines and the Radius of a Circle: | This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Parallel lines and transversals: | In this tutorial, students will find the measures of angles formed when a transversal cuts two parallel lines. |
| Parallel lines, transversals and triangles: | This tutorial shows students the eight angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. There is also a review of triangles in this video.
|
| Parallel lines and transversal lines: | Students will see in this tutorial the eight angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. |
| Parallel lines and transversals: | In this tutorial, students will learn the angle measures when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line. |
| Sum of Exterior Angles of an Irregular Pentagon: | In this video, students will learn how to use what they know about the sum of angles in a triangle to determine the sum of the exterior angles of an irregular pentagon. |
| Proving vertical angles are equal: | In this tutorial, students prove that vertical angles are equal. Students should have an understanding of supplementary angles before viewing this video. |
| Finding the measure of vertical angles: | Students will use algebra to find the measure of vertical angles, or angles opposite each other when two lines cross. Students should have an understanding of complementary and supplementary angles before viewing this video. |
| Introduction to vertical angles: | In this tutorial, students will use their knowledge of supplementary, adjacent, and vertical angles to solve problems involving the intersection of two lines. |
| Using Algebra to Find Measures of Angles Formed from Transversal: | We will use algebra in order to find the measure of angles formed by a transversal. |
| Figuring Out Angles Between Transversal and Parallel Lines: | We will be able to identify corresponding angles of parallel lines. |
| Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals: | We will gain an understanding of how angles formed by transversals compare to each other. |
| Proof: Vertical Angles are Equal: | This 5 minute video gives the proof that vertical angles are equal. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Points equidistant from two points in the plane: | This task asks students to show how certain points on a plane are equidistant to points on a segment when placed on a perpendicular bisector. |
| Tangent Lines and the Radius of a Circle: | This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. |

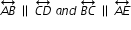 . Let
. Let 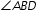 measure (3x+4)º,
measure (3x+4)º, 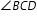 measure(6x-8)º, and
measure(6x-8)º, and 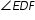 measure (7x-20)º.
measure (7x-20)º.