General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
- Translate between decimal and fraction notation, particularly when the decimals are repeating.
- Create and solve simple linear equations to find the fractional equivalent of a repeating decimal.
- Understand the effect of multiplying a decimal by a power of 10.
All irrational numbers may be used, excluding ??. Only rational numbers with repeating decimal expansions up to thousandths may be used.
No
No context
Sample Test Items (4)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Select all numbers that are irrational.
|
N/A | MS: Multiselect |
| Sample Item 2 | Which number is irrational?
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 3 | What is |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 4 | Determine whether each number is rational or irrational.
|
N/A | MI: Matching Item |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1205050: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 7 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205070: | M/J Grade 8 Pre-Algebra (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200410: | Mathematics for College Success (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022 (course terminated)) |
| 1200700: | Mathematics for College Algebra (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022 (course terminated)) |
| 7812030: | Access M/J Grade 8 Pre-Algebra (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912115: | Fundamental Explorations in Mathematics 2 (Specifically in versions: 2013 - 2015, 2015 - 2017 (course terminated)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Repeating Decimals | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to:
|
| Rational Numbers | Students are asked to identify rational numbers from a list of real numbers, explain how to identify rational numbers, and to identify the number system that contains numbers that are not rational. |
| Decimal to Fraction Conversion | Students are given several terminating and repeating decimals and asked to convert them to fractions. |
| Fraction to Decimal Conversion | Students are given a fraction to convert to a decimal and are asked to determine if the decimal repeats. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Repeating Decimals | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to translate between decimal and fraction notation, particularly when the decimals are repeating, create and solve simple linear equations to find the fractional equivalent of a repeating decimal, and understand the effect of multiplying a decimal by a power of 10. |
| Who's Being Irrational? | In this lesson, students will learn how irrational numbers differ from rational numbers. The students will complete a graphic organizer that categorizes rational and irrational numbers. Students will also be able to identify irrational numbers found in the real world. |
| Rational vs Irrational | Students will organize the set of real numbers and be able to identify when a number is rational or irrational. They will also learn the process of how to change a repeating decimal to its equivalent fraction. |
| Really! I'm Rational! | In this lesson students will gain an understanding of how repeating decimals are converted into a ratio in the form of |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Calculating the Square Root of 2 | This task is intended for instructional purposes so that students can become familiar and confident with using a calculator and understanding what it can and cannot do. This task gives an opportunity to work on the notion of place value (in parts [b] and [c]) and also to understand part of an argument for why the square root of 2 is not a rational number. |
| Estimating Square Roots | By definition, the square root of a number n is the number you square to get n. The purpose of this task is to have students use the meaning of a square root to find a decimal approximation of a square root of a non-square integer. Students may need guidance in thinking about how to approach the task. |
| Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations | Requires students to "convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number." Despite this choice of wording, the numbers in this task are rational numbers regardless of the choice of representation. For example, 0.333¯ and 1/3 are two different ways of representing the same number. |
| Identifying Rational Numbers | The task assumes that students can express a given repeating decimal as a fraction. Teachers looking for a task to fill in this background knowledge could consider the related task "Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations". |
| Calculating and Rounding Numbers | In this task, students explore some important mathematical implications of using a calculator. Specifically, they experiment with the approximation of common irrational numbers such as pi (p) and the square root of 2 (v2) and discover how to properly use the calculator for best accuracy. Other related activities involve converting fractions to decimal form and a concrete example where rounding and then multiplying does not yield the same answer as multiplying and then rounding. |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 8 | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Classifying Numbers | In this tutorial, you will practice classifying numbers as whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. |
| An introduction to rational and irrational numbers | Students will learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers. |
| Converting a fraction to a repeating decimal | Students will learn how to convert a fraction into a repeating decimal. Students should know how to use long division before starting this tutorial. |
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Irrational Numbers | Although the Greeks initially thought all numeric quantities could be represented by the ratio of two integers, i.e. rational numbers, we now know that not all numbers are rational. How do we know this? |
Student Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Calculating the Square Root of 2: | This task is intended for instructional purposes so that students can become familiar and confident with using a calculator and understanding what it can and cannot do. This task gives an opportunity to work on the notion of place value (in parts [b] and [c]) and also to understand part of an argument for why the square root of 2 is not a rational number. |
| Estimating Square Roots: | By definition, the square root of a number n is the number you square to get n. The purpose of this task is to have students use the meaning of a square root to find a decimal approximation of a square root of a non-square integer. Students may need guidance in thinking about how to approach the task. |
| Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations: | Requires students to "convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number." Despite this choice of wording, the numbers in this task are rational numbers regardless of the choice of representation. For example, 0.333¯ and 1/3 are two different ways of representing the same number. |
| Identifying Rational Numbers: | The task assumes that students can express a given repeating decimal as a fraction. Teachers looking for a task to fill in this background knowledge could consider the related task "Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations". |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 8: | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Classifying Numbers: | In this tutorial, you will practice classifying numbers as whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. |
| An introduction to rational and irrational numbers: | Students will learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers. |
| Converting a fraction to a repeating decimal: | Students will learn how to convert a fraction into a repeating decimal. Students should know how to use long division before starting this tutorial. |
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Irrational Numbers: | Although the Greeks initially thought all numeric quantities could be represented by the ratio of two integers, i.e. rational numbers, we now know that not all numbers are rational. How do we know this? |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Calculating the Square Root of 2: | This task is intended for instructional purposes so that students can become familiar and confident with using a calculator and understanding what it can and cannot do. This task gives an opportunity to work on the notion of place value (in parts [b] and [c]) and also to understand part of an argument for why the square root of 2 is not a rational number. |
| Estimating Square Roots: | By definition, the square root of a number n is the number you square to get n. The purpose of this task is to have students use the meaning of a square root to find a decimal approximation of a square root of a non-square integer. Students may need guidance in thinking about how to approach the task. |
| Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations: | Requires students to "convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number." Despite this choice of wording, the numbers in this task are rational numbers regardless of the choice of representation. For example, 0.333¯ and 1/3 are two different ways of representing the same number. |
| Identifying Rational Numbers: | The task assumes that students can express a given repeating decimal as a fraction. Teachers looking for a task to fill in this background knowledge could consider the related task "Converting Decimal Representations of Rational Numbers to Fraction Representations". |
| Calculating and Rounding Numbers: | In this task, students explore some important mathematical implications of using a calculator. Specifically, they experiment with the approximation of common irrational numbers such as pi (p) and the square root of 2 (v2) and discover how to properly use the calculator for best accuracy. Other related activities involve converting fractions to decimal form and a concrete example where rounding and then multiplying does not yield the same answer as multiplying and then rounding. |

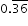 written as a fraction?
written as a fraction? by completing an exploration worksheet. They will conclude that any number which can be written in this form is called a rational number.
by completing an exploration worksheet. They will conclude that any number which can be written in this form is called a rational number.