General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
N/A
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (3)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Which expression has a coefficient of 2?
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 2 | What is the surface area, in centimeters, of a cube with a side length, s, of |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 3 | Select all the statements that describe the expression 5 +2x.
|
N/A | MS: Multiselect |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1205010: | M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205020: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 6 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200410: | Mathematics for College Success (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022 (course terminated)) |
| 7812015: | Access M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912110: | Fundamental Explorations in Mathematics 1 (Specifically in versions: 2013 - 2015, 2015 - 2017 (course terminated)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Substitution Resolution | Students are asked to evaluate formulas for given values of the variables. |
| Parts of Expressions | Students are asked to identify key parts of algebraic expressions. |
| Writing Expressions | Students are asked to write expressions that record operations with numbers and variables. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| I'll Fly Today | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will use the provided data to calculate travel time and total cost after tax. Students will consider this data and other provided criteria to assist a travel agent in determining which airline to choose for a client. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Gather Data For Distribution by Programming an App | This lesson allow students to gather, calculate, and plot data using both computer code and mathematical equations. In this lesson students will create a pedometer app to demonstrate the understanding of algorithms, components (such as buttons, textboxes, sensors, etc.), and If/Then statements. This lesson uses algebraic equations and random data to access the needed components to store data in a spreadsheet. |
| Data Sets Represented in Computers | This lesson shows how data can be represented by computers, in relation to everyday activities we may not be aware that we use computer. It gives an overview of graphing data by creating a histogram based on population data. Using the data collected, students will get a chance to hand write code to show what structure is needed for computers to collect, analyze and distribute such data. This lesson is lesson 1 of the Data Set and Deviation Statistics Unit and bridges statistical concepts of data collection, graphing and analysis with programming a computer using coding language while reinforcing foundational algebraic skills. |
| Expressions and Art | Students will design a color-by-expression picture in order to practice evaluating algebraic expressions including substitution and order of operations. |
| Lost in Translation? Verbal and Algebraic Representations of Expressions and Equations | This lesson is designed to assist in teacher facilitation of student understanding related to the concept of translating between verbal and algebraic two-step equations. |
| Going The Distance | This lesson provides a hands-on activity where students can apply solving one-step multiplication and division equations to a real-world problem. The lesson focuses on the relationship between distance, rate, and time. The students will also represent data on graphs and draw conclusions and make interpretations based on the graphs. |
| Interpreting Algebraic Expressions | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to translate between words, symbols, tables, and area representations of algebraic expressions. It will help you to identify and support students who have difficulty in recognizing the order of algebraic operations, recognizing equivalent expressions and understanding the distributive laws of multiplication and division over addition (expansion of parentheses). |
| Feel the Heat! | This MEA is a great way to implement Florida State Standards for math and language arts. It also supports cooperative learning groups and encourages student engagement. Students will explore different types of materials to determine which absorbs the least amount of heat. Students will also calculate the surface area to determine the cost for constructing the buildings using the materials. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Expressions, Phrases and Word Problems, Oh My! | This lesson focuses on using appropriate mathematical language when reading or writing expressions, with students applying this knowledge to translate written phrases into algebraic expressions and vice versa. Students will analyze word problems for key words and write the representative expressions. |
| Decoding Word Phrases-Translating verbal phrases to variable expressions | This lesson is designed to help students decode word phrases and then translate them from word form into numerical form. It provides a resource, in the form of a foldable, that can be kept all year and used anytime the students need to decode word phrases. |
| Let's Translate!! | Students will translate verbal phrases into algebraic expressions. Students are given practice in writing expressions that record operations with numbers and variables. Special attention is given to writing operations in the correct order. Class work and homework worksheets are provided with answer keys for each. |
| The n-gon Train | In this lesson, students will determine the perimeter of a train of polygons, for different regular polygons. The accompanying videos (intended audience is teachers) provide segments of an implementation of the lesson. |
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 3: If Statements | Explore computer coding on the farm by using relational operators and IF statements to evaluate expressions. In this interactive tutorial, you'll also solve problems involving inequalities. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 2: Condition Statements | Explore computer coding on the farm by using condition and IF statements in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to apply the order of operations as you using coding to solve problems. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 1: Declare Variables | Explore computer coding on the farm by declaring and initializing variables in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to practice your long division skills. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Rectangle Perimeter 1 | This tasks gives a verbal description for computing the perimeter of a rectangle and asks the students to find an expression for this perimeter. They then have to use the expression to evaluate the perimeter for specific values of the two variables. |
| Distance to School | This task asks students to find equivalent expressions by visualizing a familiar activity involving distance. The given solution shows some possible equivalent expressions, but there are many variations possible. |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 6 | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Teaching Idea
| Name | Description |
| True, False, and Open Sentences | "Students first explore arithmetic sentences to decide whether they are true or false. The lesson then introduces students to sentences that are neither true nor false but are algebraic equations, also called open sentences, such as x + 3 = 7 or 2 x = 12." from Math Solutions. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| How to Evaluate an Expression with Variables | Learn how to evaluate an expression with variables using a technique called substitution. |
| How to Evaluate Expressions with Two Variables | This video demonstrates evaluating expressions with two variables. |
| Thinking About the Changing Values of Variables and Expressions | Explore how the value of an algebraic expression changes as the value of its variable changes. |
| How to Evaluate an Expression Using Substitution | In this example, we have a formula for converting a Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit. |
| Order of Operations: PEMDAS | Work through a challenging order of operations example with only positive numbers. |
| Order of Operations | Work through a challenging order of operations example with only positive numbers. |
| Examples of evaluating variable expressions | Examples of evaluating variable expressions |
| Example: Evaluating expressions with 2 variables | Evaluating Expressions with Two Variables |
| How to evaluate an expression using substitution | In this example we have a formula for converting Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit. Let's substitute the variable with a value (Celsius temp) to get the degrees in Fahrenheit. Great problem to practice with us! |
| Evaluating an algebraic expression in a word problem | In this example of evaluating expressions, we're dusting off some geometry. On top of that, it's a word problem. We're seeing how different concepts in math are layered on top of each other to create more interesting and complex problems to solve. |
| Why aren't we using the multiplication sign? | Great question. In algebra, we do indeed avoid using the multiplication sign. We'll explain it for you here. |
| What is a variable? | Our focus here is understanding that a variable is just a letter or symbol (usually a lower case letter) that can represent different values in an expression. We got this. Just watch. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 3: If Statements: | Explore computer coding on the farm by using relational operators and IF statements to evaluate expressions. In this interactive tutorial, you'll also solve problems involving inequalities. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 2: Condition Statements: | Explore computer coding on the farm by using condition and IF statements in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to apply the order of operations as you using coding to solve problems. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 1: Declare Variables: | Explore computer coding on the farm by declaring and initializing variables in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to practice your long division skills. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Rectangle Perimeter 1: | This tasks gives a verbal description for computing the perimeter of a rectangle and asks the students to find an expression for this perimeter. They then have to use the expression to evaluate the perimeter for specific values of the two variables. |
| Distance to School: | This task asks students to find equivalent expressions by visualizing a familiar activity involving distance. The given solution shows some possible equivalent expressions, but there are many variations possible. |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 6: | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| How to Evaluate an Expression with Variables: | Learn how to evaluate an expression with variables using a technique called substitution. |
| How to Evaluate Expressions with Two Variables: | This video demonstrates evaluating expressions with two variables. |
| Thinking About the Changing Values of Variables and Expressions: | Explore how the value of an algebraic expression changes as the value of its variable changes. |
| How to Evaluate an Expression Using Substitution: | In this example, we have a formula for converting a Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit. |
| Order of Operations: PEMDAS: | Work through a challenging order of operations example with only positive numbers. |
| Order of Operations : | Work through a challenging order of operations example with only positive numbers. |
| Example: Evaluating expressions with 2 variables: | Evaluating Expressions with Two Variables |
| How to evaluate an expression using substitution: | In this example we have a formula for converting Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit. Let's substitute the variable with a value (Celsius temp) to get the degrees in Fahrenheit. Great problem to practice with us! |
| Why aren't we using the multiplication sign?: | Great question. In algebra, we do indeed avoid using the multiplication sign. We'll explain it for you here. |
| What is a variable?: | Our focus here is understanding that a variable is just a letter or symbol (usually a lower case letter) that can represent different values in an expression. We got this. Just watch. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Rectangle Perimeter 1: | This tasks gives a verbal description for computing the perimeter of a rectangle and asks the students to find an expression for this perimeter. They then have to use the expression to evaluate the perimeter for specific values of the two variables. |
| Distance to School: | This task asks students to find equivalent expressions by visualizing a familiar activity involving distance. The given solution shows some possible equivalent expressions, but there are many variations possible. |

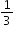 cm?
cm?