General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Figures are limited to rectangles and shapes that can be decomposed into rectangles. Dimensions of figures are limited to whole numbers. All values in items may not exceed whole number multiplication facts of 10 x 10.
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (3)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
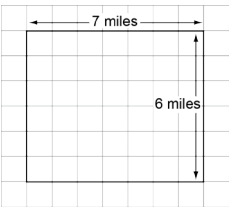
| Sample Item 1 | A park is in the shape of the rectangle shown.
What is the area, in square miles, of the park? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
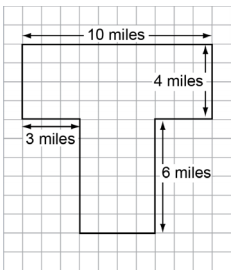
| Sample Item 2 | A park is shown.
What is the area, in square miles, of the park? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
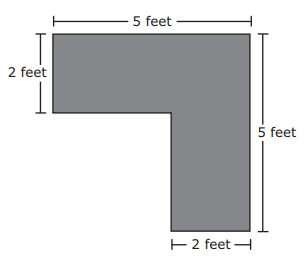
| Sample Item 3 | Specifically for MAFS.3.MD.3.7d: A drawing of the top of a desk is shown.
What is the area of the top of the desk?
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 5012050: | Grade Three Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7712040: | Access Mathematics Grade 3 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012055: | Grade 3 Accelerated Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012015: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 3-5 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Using Arrays to Model the Distributive Property | Students are presented with a rectangular area model and asked to write an equation that represents the distributive property. |
| Cover Me | Students determine the area of a rectangle in two different ways. |
| Decompose Shapes to Find Area | Students are given a rectilinear shape and asked to find its area. |
| Area of a Butterfly Garden | Students are asked to find the areas of two rectangular figures and are observed to determine if they use multiplication. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Area of Rectangles: A More Efficient Way? | In this lesson, students will connect the concepts of counting each square unit and multiplying the side lengths to compute the area of a rectangle. They will extend this knowledge by computing a side length, when given only the area and the other side length. |
| "This is InTENTS!" | This STEM challenge will engage the students in the ways to create different rectangles that have the same area, but different perimeters. They will also explore how to use scientific processes to test their designs with hypothesis, records, data, and a conclusion. This STEM challenge combines architectural engineering with life science and measurement skills for math. |
| Blowin' Around the House | In this engineering design challenge, student teams will design a house that will withstand high winds. |
| Area: Add or Multiply? | This lesson is designed to encouage students to make connections to their prior knowledge of multiplying using rectangular arrays to finding the area of rectangles by multiplying the side lengths. Students will be led to "discover" the formula for finding area. |
| From Arrays to Areas | Students will be asked to use different strategies to figure out the area of rectangles.. Students progress from playing a game with arrays, to creating rectangles with square tiles, and finally to exploring the area formula. |
| All About Area | This lesson is an introductory lesson about area at the third-grade level. Students will play a game to learn the definition of area, build with square tiles to discover we measure area with square units, and then put this knowledge in practice to complete two worksheets. |
| Best Vegetable Garden | The students will plan a vegetable garden, deciding which kinds of vegetables to plant, how many plants of each kind will fit, and where each plant will be planted in a fixed-area garden design. Then they will revise their design based on new garden dimensions and additional plant options. Students will explore the concept of area to plan their garden and they will practice solving 1 and 2-step real-world problems using the four operations to develop their ideas. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Treehouse Makeover MEA | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, The Shady Oak Treehouse Club is doing a makeover and needs help choosing flooring. Students will be asked to figure area, calculate cost, and add installation fees to cost. The students will then rank the flooring and choose the best one for the makeover. The data provided is: a model of the treehouse (in square yards), flooring price per square yard, and ratings for ease of cleaning, comfort, and color choices. In the twist, student will be provided with an installation fee for each flooring material and must decide if, and how, to change their procedure with the new information. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Area Architects, Lesson 3 | In this unit on area, students explore geometric measurement by becoming "Area Architects" in order to learn the concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and addition. This lesson is the third of a five-lesson unit. |
| Area: We Need to Know | In this lesson students build on their knowledge of area by finding the area of a variety of composite figures and create a composite shape when given an area. |
| Area of Rectangles: A More Efficient Way? | In this lesson, students will connect the concepts of counting each square unit and multiplying the side lengths to compute the area of a rectangle. |
| No Spare Space | In this lesson, the students are employees of a fencing company. They are working with a customer to try and get the best deal and design of a fence that will fit the customer's area needs. Students will have to use reasoning skills in order to fill in missing information. Students will also discuss whether or not their designs have met the needs of the customer. |
| Area Architects, Lesson 2 | In this unit on area, students explore geometric measurement by becoming "Area Architects" to learn the concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and addition. This lesson is the second of a five-lesson unit. In this lesson, students will develop strategies for finding the area of rectangles with whole-number side lengths by tiling it and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths. |
| Area Architects, Lesson 5 | In this unit on area, students explore geometric measurement by becoming "Area Architects" in order to learn the concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and addition. This lesson is the fifth and final lesson of the unit. In this lesson, students will recognize area as additive. Students will find areas of rectangular figures by decomposing them into non-overlapping parts in order to solve a real-world problem. This lesson is focused on single-digit x single-digit dimensions using proper units for dimensions (e.g. ft, yd, m) and square units for the area (e.g. sq. ft, sq. yd, sq. m). |
| Area Architects, Lesson 4 | In this 5-lesson unit on area, students explore geometric measurement by becoming "Area Architects" in order to learn the concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and addition. In this 4th lesson, students will use tiling to show in a concrete case that the area of a rectangle can be found using the distributive property of multiplication. This lesson is focused on single-digit x single-digit dimensions using proper units for dimensions (e.g. ft, yd, m) and square units for the area (e.g. sq. ft, sq. yd, sq. m). |
| Area and Perimeter of Rectangles Investigations | Students will determine the validity of the statement, "All rectangles with the same area will have the same perimeter" through two investigations. |
| Area Isn't Just for Squares | This lesson helps students make the connections between area and multiplication using square tiles. |
| House Building Architects | In this lesson, students are tasked with drawing a house based on given directions. The directions include the area and perimeter of particular features of the house. This resource is recommended as a review of perimeter and area. |
| Squiggly's New Space: A Deeper Look at Area and Perimeter | Students will use guided discovery to find a formula for both area and perimeter in order to more efficiently solve area and perimeter problems. |
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Terrific Tiling | Learn how tilling can be used to find the area of different rectangular rooms in this interactive tutorial. |
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Connecting area to multiplication | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, students who understand how to count unit squares to find the area of a rectangle can explore the connection between this method and the area formula for rectangles (length times width or base times height). |
Worksheet
| Name | Description |
| Junior Architects: Finding Perimeter and Area | In this worksheet, students are directed to find the perimeter and area for a clubhouse in the form of rectangles, composite figures, and other polygons. The second sheet urged them to make their own designs for a clubhouse and find the perimeter and area. This resource is recommended as an introduction or review of perimeter and area. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Terrific Tiling: | Learn how tilling can be used to find the area of different rectangular rooms in this interactive tutorial. |
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Connecting area to multiplication: | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, students who understand how to count unit squares to find the area of a rectangle can explore the connection between this method and the area formula for rectangles (length times width or base times height). |
Worksheet
| Name | Description |
| Junior Architects: Finding Perimeter and Area: | In this worksheet, students are directed to find the perimeter and area for a clubhouse in the form of rectangles, composite figures, and other polygons. The second sheet urged them to make their own designs for a clubhouse and find the perimeter and area. This resource is recommended as an introduction or review of perimeter and area. |
Parent Resources
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Connecting area to multiplication: | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, students who understand how to count unit squares to find the area of a rectangle can explore the connection between this method and the area formula for rectangles (length times width or base times height). |