General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Circle
- Rectangle
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to extend the work from grade 1 of partitioning circles and rectangles. At this grade level, students will partition into three equal-sized parts, name the parts as three thirds and describe the whole (MTR.5.1).- Instruction includes the use of manipulatives such as geoboards, fraction circles, pattern blocks or color tiles, along with contextual sharing situations.
- Instruction includes the idea of part-whole relationships as supported by a model.
- Naming the parts is based on the number of equal parts that make the whole.
- Students are not expected to use formal fraction notation until grade 3.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may have difficulty partitioning into equal-sized parts.
- Students may not understand that the parts can be equal parts even if they do not look identical.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes geoboards to partition rectangles and circles into thirds.
- Instruction includes graph paper to divide shapes into equal parts when given part of a
whole by counting the units inside the shape.
- For example, the shape is a total of 30 units and one equal part is given. Students partition the shape into 3 equal parts using the knowledge that one part is equal to 10 units.

- Teacher provides opportunities to use fraction manipulatives to develop understanding of thirds in circles and rectangles.
- For example, teacher provides pictures of circles and rectangles (of the same size as the manipulatives) on a sheet of paper. Students then use the “thirds” manipulatives to trace the thirds into the circles and rectangles, so they develop an understanding of how to partition these shapes into thirds.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.2.1)
Provide students with paper copies of circles and rectangles.- Part A. Cut or fold the figures to determine how one can create two, three or four equal- sized parts.
- Part B. Use mathematical language to describe the parts created in Part A.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Is Shape A or Shape B partitioned into four fourths? Explain your thinking.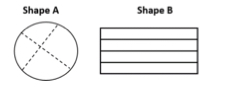
Instructional Item 2
Below is one-half of a whole. Draw two halves to make a whole. Encourage students to provide two different ways to make a whole.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
