
|
Generated on 7/31/2025 at 8:52 AM |
The webpage this document was printed/exported from can be found at the following URL:
https://www.cpalms.org//PreviewStandard/Preview/15809
https://www.cpalms.org//PreviewStandard/Preview/15809
Construct proofs, including proofs by contradiction.
Standard #: MA.912.LT.4.8
Standard Information
Standard Clarifications
Clarification 1: Within the Geometry course, proofs are limited to geometric statements within the course.
General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 912
Strand: Logic and Discrete Theory
Standard: Develop an understanding of the fundamentals of propositional logic, arguments and methods of proof.
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Standard Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In grades 7 and 8, students explored the reasons why some geometric statements concerning angles and polygons are true or false. In Geometry, students learn and construct proofs for many of the geometric facts that they encounter. The content of this benchmark is to be used throughout this course. In later courses, students continue to learn and construct proofs in many different areas.- Instruction includes the student understanding that proofs and proofs by contradiction can
be represented in various ways. Students should have practice with each type of proof,
understanding when one may be a more effective way to present information. (MTR.2.1)
- Two-column proofs
Organize the reasoning in two columns: statements and reasons. Each statement has a corresponding reason, and the proof usually starts with the given information.
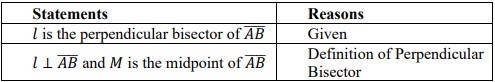
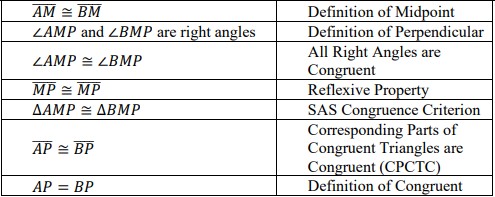
For example, given the perpendicular bisector of AB, , prove: AP = BP
- Pictorial proofs
Visual way to express the proof in its entirety. The picture can be accompanied by an explanation to provide background information or indicate the reasoning depicted by the picture. For example, the proof of the Pythagorean Theorem can be expressed as shown below.Both squares have the same side length, + , so they have the same area. The white region in each square consists of four right triangles (I, II, III and IV), therefore the area of the white region in both squares is the same. Students can conclude the area of the grey region in each square is also the same showing that 2 + 2 = 2.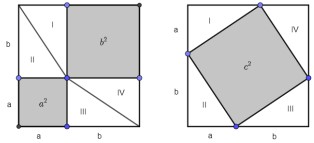
- Paragraph and narrative proofs
Consists of a logical argument written as a paragraph, giving evidence and detailed reasons to draw a conclusion. Paragraph proofs can be seen as a twocolumn proof written in sentences. - Flow chart proofs
A way to organize statements and reasons needed in a structured way to indicate the logical order. Statements are placed in boxes, reasons are placed under the box, and arrows are used to represent the flow or progression of the argument.
For example, the proof that vertical angles are congruent is shown below.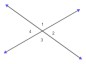
- Informal proofs
A way to provide convincing evidence to show that something is true. Informal proofs include the use of manipulatives, drawings and geometric software.
- Two-column proofs
- Instruction includes the understanding that when a proof cannot be proved directly, it
may be able to be proved by contradiction. A proof by contradiction assumes that the
statement to be proved is not true and then uses a logical argument to deduce a
contradiction. The logical argument can be represented in any form of a proof: twocolumn, pictorial, paragraph and flow chart.
- For example, if students want to prove by contradiction that BC
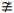 ST given two
triangles ABC and RST, with AC ≅ RT, AB ≅ RS and ∠A
ST given two
triangles ABC and RST, with AC ≅ RT, AB ≅ RS and ∠A 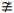 ∠R, they can start by
assuming that BC ≅ ST. Under this assumption, ΔABC ≅ ΔRST by Side-Side-Side since AC ≅ RT and AB ≅ RS were given. Since the two triangles are
congruent and corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent (CPCTC),
then students can conclude that ∠A ≅ ∠R. Students should realize that this
contradicts the given information, ∠A
∠R, they can start by
assuming that BC ≅ ST. Under this assumption, ΔABC ≅ ΔRST by Side-Side-Side since AC ≅ RT and AB ≅ RS were given. Since the two triangles are
congruent and corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent (CPCTC),
then students can conclude that ∠A ≅ ∠R. Students should realize that this
contradicts the given information, ∠A 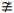 ∠R. Therefore, this contradiction shows
that the statement BC ≅ ST is false, proving that BC
∠R. Therefore, this contradiction shows
that the statement BC ≅ ST is false, proving that BC 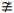 ST is true.
ST is true.
- For example, if students want to prove by contradiction that BC
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may determine the statement of contradiction incorrectly.
- For example, when completing a proof by contradiction, a student may create the statement of contradiction from one of the given pieces of information rather than what is to be proven.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.2.1, MTR.4.1)- A pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal as shown.
 0
0- Part A. Using the Linear Pair Postulate and postulates involving parallel lines, prove that angle 1 is congruent to angle 8.
- Part B. Compare your proof with a partner.
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.3.1)
- Order the following statements to prove by contradiction that a triangle can only have one right angle.
- The measure of angle K is 90°.
- The measure of an angle in a triangle cannot equal 0°.
- In triangle JKL, only one of the angles can be a right angle.
- ∠J + ∠K + ∠L = 180°
- Assume triangle JKL has two right angles, angle J and angle K.
- The measure of angle J is 90°.
- 90° + 90° + ∠L = 180°
- A triangle cannot have more than one right angle.
- ∠L = 0°
- The sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle is 180°.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- Use a proof by contradiction to prove the following statement.An equilateral triangle cannot also be a right triangle.
Related Courses
- Geometry Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) # 1206320
- Discrete Mathematics Honors (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) # 1212300
- Philosophy Honors Logic (Specifically in versions: 2025 and beyond (current)) # 2105342