General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Circle
- Dilation
- Similarity
- Translation
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In grade 8, students learned about similarity and similarity transformations. In Geometry, students apply transformations to prove that all circles are similar.- Instruction includes presenting students with a pair of circles of different size and asking them to identify a sequence of transformations that would map one onto the other. Students should realize that a single translation and a single dilation is all that is needed in a sequence to map one onto the other.
- Instruction includes the connection to the coordinate plane by showing that two circles are similar using coordinates.
- Students should connect the definition of similarity in terms of corresponding parts
applied to polygons and explore what parts of the circles will be in proportion between
the preimage and image of a dilations.
- For example, given two circles, their radii (1 and 2) and their diameters (1 and
2) would satisfy the proportional relationship
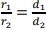 .
.
- For example, given two circles, their radii (1 and 2) and their diameters (1 and
2) would satisfy the proportional relationship
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may think that always need a formal proof to prove that all circles are similar.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.4.1)- Two concentric circles with point A as the center and circle B are given on the coordinate plane.
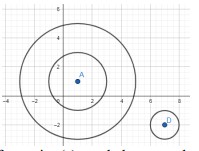
- Part A. Describe the transformation(s) needed to map the smaller circle A onto the larger circle A.
- Part B. List the transformation(s) that could be used to show that each circle A is similar to circle D. Compare your transformations with a partner.
- Part C. What is the difference in the transformation(s) depending on the circle A chosen?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- Circle A and circle D are given below.
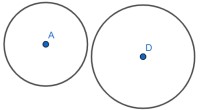
- Part A. Describe a set of transformations that could be used on circle A to show it is similar to circle D.
- Part B. Describe a set of transformations that could be used on circle D to show it is similar to circle A.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
