General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Linear Equation
- Rotation
- Slope
- Translation
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In grade 8, students determined whether a graphed system of linear equations resulted in one solution, no solution (parallel lines) or infinitely many solutions. In Algebra I, students write linear two-variable equations that are parallel or perpendicular to one another. In Geometry, students will use slope criteria of parallel and perpendicular lines to justify postulates, relationships or theorems.- Instruction includes allowing students to explore the transformations of two lines using
graphing software or other technology. If students don’t have their own computers, use
your own and let students direct the exploration.
- For example, using graphing software, ask students to use the sliders to discover two lines that are parallel. Once students achieve this, write the equations of these two lines on the board and ask them to find two different lines that are parallel. Write the equations for these lines on the board. Repeat this for multiple pairs of lines. As students explore, ask them to find patterns in the equations they develop (MTR.5.1). Guide their discussion to focus on the fact that parallel lines have equivalent slopes (MTR.4.1).
- Repeat this exercise for perpendicular lines.
- When students establish connections and understanding of slopes of parallel and
perpendicular lines, tie them back to their work with transformations in Grade 8
(MTR.5.1).
- For example, parallel lines can be translated to coincide with each other without changing slope.
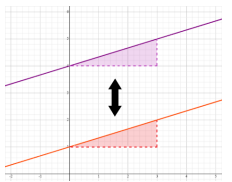
- For example, perpendicular lines can be rotated 90° about the point of intersection
to coincide with each other. Use slope to draw congruent triangles on each line
and show the change in slope to an opposite reciprocal after rotation.
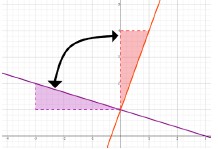
- For example, perpendicular lines can be rotated 90° about the point of intersection
to coincide with each other. Use slope to draw congruent triangles on each line
and show the change in slope to an opposite reciprocal after rotation.
- Once students understand slope relationships, instruction should guide them to utilize
slope and a point on the line to develop the point-slope equation for the line.
- Students can also develop slope-intercept equations for the line. Students should have prior knowledge from their work in MA.912.AR.2.2 that and in a linear equation represent points on the corresponding line. Direct students to see that substituting the slope of a line () and the coordinates of a point on that line (, ) into slope-intercept form ( = + ) allows them to solve to find the -intercept.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Some students may forget to change the sign of the slope when working through perpendicular line problems. Others may change the sign correctly but forget to make the slope a reciprocal. In both cases, consider having the student sketch a rough graph or use graphing software to check their result.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction provides opportunities to identify parallel or perpendicular lines using a graphing tool, graphing software or sketching a rough graph.
- Instruction includes opportunities to graph a linear function on a coordinate grid.
Teacher models using a piece of spaghetti or other straight item (such as a pencil) to
show a line parallel or perpendicular to the one they graphed and estimate the slope of
the straight item. Students can compare that estimate with the slope of the parallel or
perpendicular line they determined algebraically.
1
- For example, if the given line has a slope of − and the student determines incorrectly that the perpendicular slope is −2, they can visually see the mistake when using a straight object that is placed perpendicular to the graph of the given line.
- Teacher provides opportunities to practice identifying the slope of parallel and
perpendicular lines using a graphic organizer. To follow up this activity, have students
do a card match where they match a linear equation to the slope of a parallel line and the
slope of a perpendicular line.
- For example, the organizer below could be used to identify the slope of the
parallel and perpendicular line of the given equation.
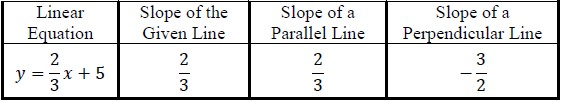
- For example, the organizer below could be used to identify the slope of the
parallel and perpendicular line of the given equation.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.3.1)- Write a linear function for a line that is parallel to () = − 8 and passes through the 3 point (−7, 0).
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1)
- Part A. A vertical line that passes through the point (−0.42, 7.8) is perpendicular to another line. What could be the equation of the second line?
- Part B. Graph both lines on a coordinate plane. What do you notice about the lines?
- Part C. Compare your graph with a partner
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- Write a linear function for a line that passes through the point (4, –3) and is perpendicular to = 0.25 + 9.
Instructional Item 2
- Write an equation for the line that passes through (3, 14) and is parallel to the line that passes through (10, 2) and (25, 15).
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
