General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Axes (of a graph)
- Coordinate Plane
- Coordinate
- Origin
- Quadrant
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In grade 5, students plotted and labeled ordered pairs of whole numbers in the first quadrant. Students in grade 6 plot ordered pairs of rational numbers in all four quadrants. In grade 7, students will apply their knowledge of the plotting of ordered pairs to the graphing of proportional relationships.- Instruction includes making connections to opposites on a number line and absolute value, as well as to reflections across the -and -axes.
- Instruction includes using academic terminology including calling ordered pairs as coordinates and as a coordinate pair.
- Instruction includes students’ plotting ordered pairs on graphs with different scales.
- For example, students can plot the ordered pair ( , 3), where the -and -axis have a scale of 2 or a scale of 0.5.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may switch the location of the -coordinate and the -coordinate in the ordered pair.
- Students may misunderstand that a point on an axis has at least one coordinate of zero.
- For example, the point on the graph identified as (3,0) may have a student incorrectly identify the location as (3,3) or just 3.
- Students may misunderstand the numbering of the four quadrants (upper right in a counter-clockwise rotation) as well as which coordinate is positive and which coordinate is negative.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher creates an anchor chart while students create their own graphic organizer to include key features of a coordinate plane. Features include the -axis, -axis, origin, quadrants, and an ordered pair.
- Instruction includes building connections to plotting points on number lines. On one sheet of tracing paper, label a horizontal number line as the ??-axis and plot the -value. On another sheet of tracing paper, label a vertical number line as the -axis and plot the -value. Overlap the two number lines with a point of intersection at the origin (0,0). Place a third sheet of tracing paper on top of the two number lines, trace and label the - and -axis to produce a coordinate plane. The location of a new point should then be plotted in the appropriate quadrant to represent the horizontal and vertical locations of the two previously plotted points. This same strategy helps to draw connections to a point laying on an axis if one of the coordinates is zero.
- Teachers may provide instruction on using reasonable estimations when plotting rational coordinates on the coordinate plane.
- For example, if a student is plotting −4 for an -value and 3 for -value, they need to know that is more than half, so to graph the -value, they should plot a point between −4 and −5, with the point closer to the −5. Then the student can more precisely adjust the point if necessary (if any other value is between −4 and −5 they can adjust, but if not, they will see that their estimation will be a valid way to order.)
- When plotting rational coordinates, teacher provides a coordinate plane with an appropriate scaling to match the fractional or decimal units so the points graphed will fall on the intersection of two minor grid lines.
- For example, if a student is graphing the ordered pair (−0.5, 2.25) the -and -axis could have a scale of 0.25.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.3.1)- (2 , )
- (−4, 5)
- (−4, −7)
- (,−5)
- (0, 0)
- (2, −8)
- (0, 0.6)
- (−4, −5)
Part C. Which points are in quadrant III?
Part D. Which points are a reflection of each other and over which axis are they reflected?
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1)
Part A. Create a picture with fewer than 20 coordinates in the four quadrants. Write your coordinates on a separate piece of paper.
Part B. Trade your list of ordered pairs with a partner. Recreate your partner’s picture on a new sheet of graph paper.
Part C. Discuss differences and discuss possible errors you or your partner may have made when recreating each other’s pictures.
Instructional Task 3 (MTR.4.1)
If given > 0 and > 0, in which quadrant or axis will each ordered pair described below lie? Explain your answer.
a. (−, )
b. (−, 0)
c.(, −)
d. (0, )
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1What is the value of the -coordinate of the ordered pair that reflects (5,−8) over the -axis?
Instructional Item 2
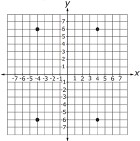
Using the graph below, state the ordered pair that describes the point plotted in Quadrant II?
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
