Write and solve one-step equations in one variable within a mathematical or real-world context using addition and subtraction, where all terms and solutions are integers.
Examples
The equations -35+x=17, 17=-35+x and 17-x=-35 can represent the question “How many units to the right is 17 from -35 on the number line?”
Clarifications
Clarification 1: Instruction includes using manipulatives, drawings, number lines and inverse operations.
Clarification 2: Instruction includes equations in the forms x+p=q and p+x=q, where x,p and q are any integer.
Clarification 3: Problems include equations where the variable may be on either side of the equal sign.
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 6
Strand: Algebraic Reasoning
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Additive Inverse Property
- Addition Property of Equality
- Associative Property
- Commutative Property of Addition
- Equation
- Identity Property of Addition
- Integer
- Number Line
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In grade 5, students wrote and evaluated numerical expressions with positive rational numbers. Students also wrote equations to determine an unknown whole number. In grade 6, students extend their understanding to solve one-step equations which include integers. In grade 7, students write and solve one-step inequalities and two-step equations involving rational numbers.
- When students write equations to solve real-world and mathematical problems, they draw on meanings of operations that they are familiar with from previous grades’ work.
- Problem types include cases where students only create an equation, only solve an equation and problems where they create an equation and use it to solve the task. Equations include variables on the left or right side of the equal symbol.
- Use models or manipulatives, such as algebra tiles, bar diagrams, number lines and balances to conceptualize equations (MTR.2.1).
- Algebra Tiles
− 3 = −10

- Bar Diagrams
− 4 = −13

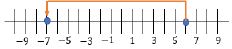
- Number Lines
+ 6 = −7
- Balances
+ 3 = −9

Students should understand the equal sign represents the fulcrum in the center of the balance and the scale is supposed to stay balanced even when you manipulate the expression on the pan of the balance (MTR.2.1).
- Instruction includes students identifying the properties of operations and properties of equality being used at each step toward finding the solution. Explaining informally the validation of their steps will provide an introduction to algebraic proofs in future mathematics (MTR.5.1).
- Students should be encouraged to show flexibility in their thinking when writing equations.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may incorrectly apply an operation to a single side of an equation.
- Students may incorrectly use the addition and subtraction properties of equality on the same side of the equal sign while solving an equation. To address this misconception, use manipulatives such as balances, algebra tiles, or bar diagrams to show the balance between the two sides of an equation (MTR.2.1).
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes identifying unknowns, constants, negative values, and mathematical operations in the provided context.
- Teacher provides opportunities for students to comprehend the context or situation by engaging in questions such as:
- What do you know from the problem?
- What is the problem asking you to find?
- Are you putting groups together? Taking groups apart? Or both?
- Are the groups you are working with the same sizes or different sizes?
- Can you create a visual model to help you understand or see patterns in your problem?
- Teacher provides opportunities for students to use algebra tiles to co-solve provided equations with the teacher without the need of writing the equation first.
- Teacher provides opportunities for students to co-write an algebraic equation with the teacher without requiring students to solve the equation.
- Teacher models the use of manipulatives such as balances, algebra tiles, or bar diagrams to show the balance between the two sides of an equation.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.2.1, MTR.4.1)- Melvin wants to go to the school musical. The school auditorium has 1250 seats arranged in three sections. The left section has 375 seats, and the right section has 375 seats. Write an equation to find the number of seats in the center section and explain why you wrote the equation the way you did.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- Given + 15 = 3, what is the value of ?
Instructional Item 2 - Given 6 = − 13, what is the value of ?
Instructional Item 3 - Alex has some money in his wallet. His grandmother gives him $10 for a gift in his birthday card. He now has $28 in his wallet. Write an equation to represent the problem. How much money did he originally have in his wallet?
Instructional Item 4 - The width of the rectangular table top is 4 feet shorter than its length. If the length of the table top is 6 feet, write and solve an equation to determine the width of the table top.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 |
Course Title222 |
| 1205010: | M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205020: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 6 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7812015: | Access M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
Related Access Points
| Access Point Number |
Access Point Title |
| MA.6.AR.2.AP.2 | Solve real-world, one-step linear equations using addition and subtraction involving integers. |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name |
Description |
| Equally Driven | Students are asked to solve a real-world problem by writing and solving an equation. |
| Center Section | Students are asked to solve a real-world problem by writing and solving an equation. |
Lesson Plans
| Name |
Description |
| How Will the Ninja Capture the Valuable Princess? | This lesson allows students to solve two-step equations involving a mythological story line in which the princess (variable) is protected by a bodyguard (number added or subtracted in an equation) and by a protector (number multiplied or divided by the variable). The three characters live in a castle, surrounded by the moat (equal sign) and an innocent bystander that lives outside the castle (number on the opposite side of the variable). However, Ninjas are infiltrating the castle to steal the “valuable” princess. Using this story line, students must then decide who the Ninja must eliminate first to get to the princess. This lesson can also be used to solve equations with like terms on the same side and equations with the same variable on each side. |
| It's All About Balance! | Students will use a balance scale graphic organizer to solve for the unknown (variable) in addition and subtraction equations with one variable. |
| Solving Addition and Subtraction Equations with Beans | Students will use dried white and black beans to solve one-step addition and subtraction equations to realize the Addition Property of Equality and Subtraction Property of Equality through the use of inverse operations (zero pairs).
|
| Bake Sale | Students will apply and develop strategies to write and solve equations for mathematical and real world situations. Students will be encouraged to use various strategies, including using inverse operations, to find a solution. |
| Capture the Boat - Sink the Teacher's Fleet! | In this lesson, students learn about the four quadrants of a coordinate plane and how to plot points in those quadrants. Students also learn how to use linear equations to predict future input and output pairs. Students work together to try to sink the teacher's fleet in a Battleship-type game while the teacher tries to sink theirs first. |
Original Student Tutorials
Perspectives Video: Teaching Idea
| Name |
Description |
| Adding Integers | Unlock an effective teaching strategy for using patterns to help students make generalizations when adding integers in this Teacher Perspectives video for educators. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name |
Description |
| Busy Day | Students are asked to write and solve an equation in one variable to answer a real world question. |
| Morning Walk | Students are asked to write an equation with one variable in order to find the distance walked. |
Tutorial
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name |
Description |
| Busy Day: | Students are asked to write and solve an equation in one variable to answer a real world question. |
| Morning Walk: | Students are asked to write an equation with one variable in order to find the distance walked. |
Tutorial
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name |
Description |
| Busy Day: | Students are asked to write and solve an equation in one variable to answer a real world question. |
| Morning Walk: | Students are asked to write an equation with one variable in order to find the distance walked. |




