General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Area Model
- Perimeter
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to understand how to work with fractional and decimal sums and products when calculating perimeter and area. This benchmark connects to previous work where students found areas and perimeters with whole number side lengths in grade 4 (MA.4.GR.2.1) and prepares for future work of finding area and perimeter on a coordinate plane in grade 6 (MA.6.GR.1.3).- During instruction, teachers should encourage students to use models or drawings to assist them with finding the perimeter and area of a rectangle and have them explain how they used the model or drawing to arrive at the solution getting them to understand that multiplying fractional side lengths to find the area is the same as tiling a rectangle with unit squares of the appropriate unit fraction side lengths (MTR.5.1).
- This benchmark provides a natural real-world context and also a visual model for the multiplication of fractions and decimals. When finding the area, teachers can begin with students modeling multiplication with whole numbers and progress into the fractional and decimal parts, such as area models using rectangles or squares, fraction strips/bars and sets of counters.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may believe that multiplication always results in a larger number. Working with area provides them with concrete situations where this is not true.
- For example a city block that is mile by mile has an area of 100 of a square mile.
- Students may have difficulty connecting visual models to the symbolic representation using equations. Use concrete visuals to represent problems.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction provides opportunities to use concrete visuals to represent problems. Instruction includes providing a rectangle to divide into fractional parts. The teacher provides students with fractional dimensions to divide the figure into to find the area of part of the whole figure. Before calculating the area, students explain if the area will be greater or less than one of the dimensions and explain how they know.
- For example, the teacher provides students with a blank rectangle and has students divide into fractional parts as shown below. The teacher uses prompts like those shown to help guide the students. After dividing the figure, the students use two different colors to shade the fractional parts and label each side with the shaded dimensions ( or ).
- Divide the figure vertically into eights. Divide the figure horizontally into sixths. Shade vertically and horizontally. The area of × is where the 2 shaded sections overlap. Is the shaded area greater or less than ? How do you know?

- Instruction includes providing fractional area models printed on transparency sheets. Models include equal size wholes divided into thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, eighths, tenths, and twelfths. Students use two transparencies to show the area of given dimensions.
- For example, the the teacher asks students to find the area of a figure with side lengths of inch and inch. Students model × by shading of one fraction model and of another fraction model. The teacher has students explain if the area will be greater or less than and explain how they know. The students then overlap the two figures and determine the fractional parts that overlap as being the area.
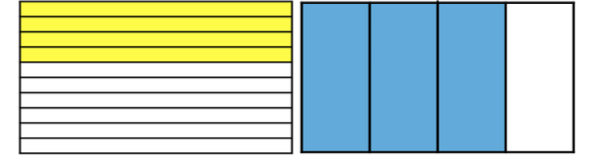
- Image showing overlapping , is overlapping.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.3.1)
Margaret draws a rectangle with a length of 5.2 inches. The width of her rectangle is one-half its length.- Part A. Draw Margaret’s rectangle and show its dimensions.
- Part B. What is the perimeter of her rectangle in inches?
- Part C. What is the area of her rectangle in square inches?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
What is the area of the square below?*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
