General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equation
- Equal Sign
- Expression
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to build relational thinking. In grade 1, students determined an unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction problem within 20.- Instruction includes an unknown value in any position.
- Instruction includes compensation of values to balance equations.
- Instruction includes the use of number lines, drawings, or models to solve addition and subtraction problems.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may confuse the value on one side of the equation with an unknown number.
- Students may think equivalent values have to look identical.
- Students may incorrectly use compensation to add or subtract.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher provides opportunities to draw quantities in an equation and use drawings to determine the unknown. Teacher provides an organizer to help students represent the quantities.
- For example, 5 + 7 = ___ + 9.
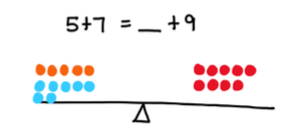
- Teacher provides opportunities to create a drawing to represent an equation by decomposing numbers on each side. The focus should be on the quantities being equal even though they look different.
- For example, 20 + 7 = 10 + 17.
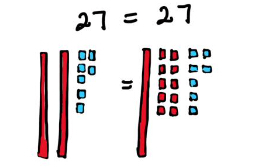
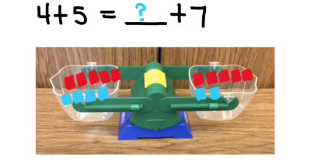
- Teacher provides opportunities to use a number balance to support understanding of finding an unknown quantity in a balanced equation.
- For example, students build the equation 4 + 5 = ____ + 7 on a number balance. Students then determine the value of the unknown quantity by balancing the number balance. This builds understanding that the two sides of the equation must be equal. If students try to use 9 as the unknown quantity, it will not balance.
- Teacher provides number strings to teach compensation strategies based on number relationships. The teacher may reveal one line at a time and give students time to think about their responses. As students move through the string, the teacher asks questions to help draw attention to the target strategy of compensation. Students illustrate their thinking using manipulatives such as base 10 blocks or illustrations.
- Example:
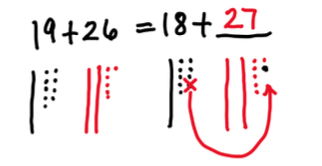
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.5.1)
A student solved for the missing addend in 30 + 43 = 26 +__ . The student says the missing addend is 47 because 26 is 4 less than 30, so we can add 4 more to 43 and that is 47. Using this strategy determine the missing addend in the equation below and justify your thinking.
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1)
Provide students the opportunity to use other strategies to determine the unknown in the equation 16 + 37 = __+ 38. Allow students to discuss which method they prefer.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Solve for the number in the blank that makes the equation true. Explain using models or drawings.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.

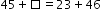 .
.