General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Number line
- Natural Number
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to introduce rounding as an estimation strategy, creating a number that is easier to compute mentally and check for reasonableness. In grade 1, students were only expected to plot, order and compare numbers to 100.- Instruction includes the use of a number line to help students determine the nearest 10.
- Instruction includes the use of real-world context to help students make sense of how a rounded number may be less precise but easier to use.
- Instruction includes cases where students must provide numbers that would round to a given number.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may round down instead of up when there is a 5 in the ones place.
- Students may not be able to identify which two tens a number is between.
- For example, a student may not be able to determine that 72 is between 70 and 80.
- Students may look at the digit in the tens place to determine how to round, rather than the ones place.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
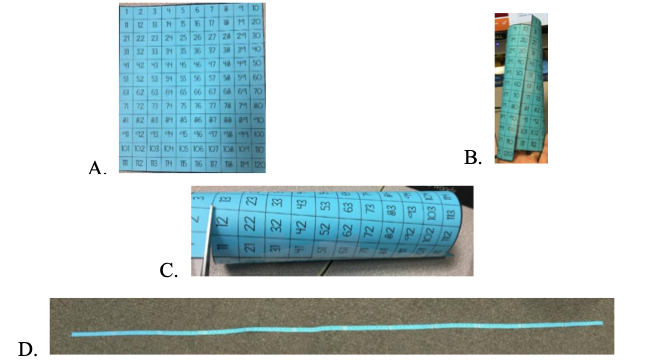
- Instruction includes using a hundreds chart and showing the relationship of 10 and the next decade. Students will use the number line/number path to clarify where a number is rounded to. Images below show how to take a 120 chart into a number path/number line.
A. Top down 120 chart. Teacher can have students highlight column of tens and the column of 5s to help with rounding when cut into a number line.
B. Line the consecutive numbers up from one decade to the next and tape.
C. Cut the number path/number line.
D. The number path/number line end result.
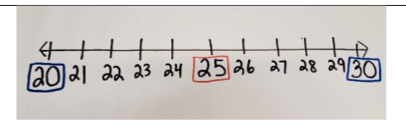
- For example, after demonstrating how the hundreds chart is a stacked number line/number path, have students find the number 43 on the number line. Ask if it rounds to 40 or 50.
- Instruction includes using a number line and base ten blocks. Using the base ten blocks on the number line, students will represent a number and reference its location to 10.
- For example, using a number line and base ten blocks teacher asks students to represent the number 27. Students will then need to determine if 27 is closer to 20 or 30 by answering how far from 20 versus 30 that 27 is. (i.e. 27 is 7 away from 20 and 3 away from 30
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.6.1)
Provide students with three sets of number cards with the digits 0-9.- Part A. Create various two-digit numbers from two of the sets of number cards provided. Plot each of the numbers on a number line.
- Part B. Round each number created from Part A to the nearest 10. Explain why each number rounds to the identified ten.
- Part C. Create a two-digit numbers from one of the sets of number cards provided. Use the other sets to create the closest rounding to nearest 10. Explain why each number rounds to the identified ten.
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.6.1)
1. Provide students with three sets of digit cards 0-9. Given a target multiple of 10, have students create at least three numbers that would round to the target. One number must have a different tens digit than the other two. (i.e. given 40 as the target, students could make the numbers 37, 39 and 42)
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Use the number line below to plot 3 numbers that would round to 30 when rounded to the nearest 10.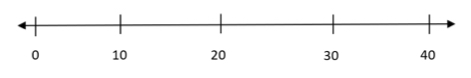
Instructional Item 2
Jamie has a collection of 52 stickers. Rounded to the nearest 10, about how many stickers does Jamie have?Instructional Item 3
Select the numbers that would round to 50 when rounded to the nearest 10.
? 42
? 49
? 44
? 45
? 58
? 51
