Identify, compare and sort two- and three-dimensional figures based on their defining attributes. Figures are limited to circles, semi-circles, triangles, rectangles, squares, trapezoids, hexagons, spheres, cubes, rectangular prisms, cones and cylinders.
Clarifications
Clarification 1: Instruction focuses on the defining attributes of a figure: whether it is closed or not; number of vertices, sides, edges or faces; and if it contains straight, curved or equal length sides or edges.
Clarification 2: Instruction includes figures given in a variety of sizes, orientations and non-examples that lack one or more defining attributes.
Clarification 3: Within this benchmark, the expectation is not to sort a combination of two- and three-dimensional figures at the same time or to define the attributes of trapezoids.
Clarification 4: Instruction includes using formal and informal language to describe the defining attributes of figures when comparing and sorting.
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 1
Strand: Geometric Reasoning
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Circle
- Cone
- Cube
- Cylinder
- Edge
- Hexagon
- Rectangle
- Rectangular Prism
- Square
- Sphere
- Trapezoid
- Triangle
- Vertex
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to recognize figures by their defining attributes as this will help them sort figures based on attributes rather than orientation, color or size. In Kindergarten, students identified circles, triangles, rectangles, squares, spheres, cubes, cones, and cylinders by a defining attribute (
MTR.2.1,
MTR.5.1).
- Instruction includes a variety of examples and non-examples that lack a defining attribute.
- While the K-12 Glossary uses the inclusive definition of a trapezoid, students will not formally identify or classify trapezoids until grade 3.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
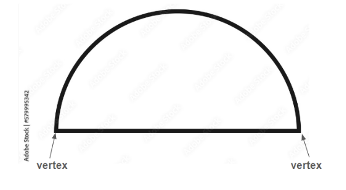
- Students may only recognize a figure by its size or orientation. In these cases, students need practice in locating figures by a defining attribute like “find the two-dimensional figures with three vertices” rather than find the triangles. Students may struggle with formal language as they are introduced to content specific vocabulary. For example, when learning the definition for vertex as defined in the K-12 Glossary as “the point at which the rays or sides of an angle, the sides of a two-dimensional figure, or the edges of a three-dimensional figure meet”, and seeing examples of vertices, students may only assume vertices can occur on figures with straight sides. A circle has no vertices, so they may assume that a semi-circle also has no vertices. However, a semi-circle has 2 points where the sides of the figure would meet, as shown below.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher may provide students with a collection of two-dimensional shapes to do the following activities in order:
- Begin “Collect and Display” by asking the students to sort the shapes into groups any way they like. Then be prepared to capture the language they use in describing the shapes (i.e. students may create a group that includes squares and rectangles because they all have “corners”). Generate a list of the informal language used here and display it on chart paper next to the shapes being used.
- Ask the students which words were important to know as they did their sort. As students respond, annotate on the chart paper and shapes to help them make the connection. For example, a student might refer to “corners” as something that helped them create their group of rectangles and squares. Write the formal term next to the student language on the chart to help them make the connection to vocabulary. The teacher might write “vertex” next to the word “corner” in the above example.
- Keep and display the chart for future activities and remind the students to borrow language from the chart as needed.
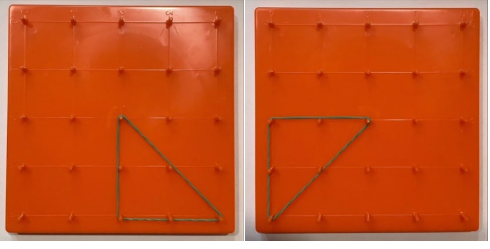
- Instruction provides opportunities to build shapes on a geoboard as the teacher calls out
defining attributes (i.e., “make a two-dimensional figure with three vertices”). After
creating a correct figure, the teacher has students rotate the geoboard 45 degrees to see
that it is still the same figure.
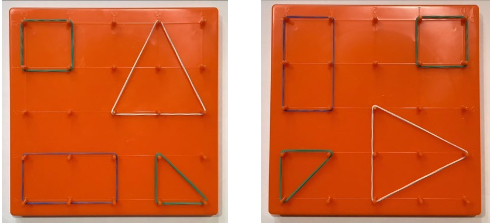
- Teachers may limit the amount and types of shapes built on the geoboard (i.e., only build
a square or triangle) if students have difficulty with multiple shapes.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.4.1)
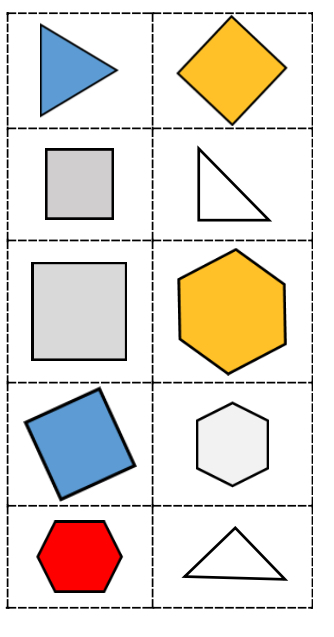
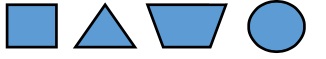
Provide students pictures of figures like the one provided to the right.
- Part A. Sort the figures by ones that have three sides and ones that have four or more sides.
- Part B. Discuss what they notice about the figures they sorted that have three sides. What is a two-dimensional figure called that has three sides? Ask students what they notice about the triangles. Are they all the same size? Do they all look the same? What makes them triangles?
- Part C. Have students look at the figures they sorted in the “four or more sides” pile. What could these figures be sorting further by? Once students determine an attribute they can sort by, have students sort by that attribute.
- Part D. How did you sort the figures? Ask students what they notice about the figures. Are they all the same size? Do they all look the same? Are they all the same figure?
- Part E. Discuss which attributes put all of the same figures together and which did not. Have students take their sorted shapes to create a pictograph by stacking their shapes on top of each other.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Which of the figures below is a trapezoid? How do you know?
Instructional Item 2
This is a cone. What makes this a cone?

Instructional Item 3
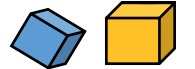
Jill says these two shapes are both cubes. Do you agree with her? Why or why not?
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
Related Courses
Related Access Points
| Access Point Number |
Access Point Title |
| MA.1.GR.1.AP.1 | Sort and identify two- or three-dimensional figures based on their defining attributes. (e.g., number of sides, vertices, edges, faces, etc., rather than color, orientation or size). Figures are limited to circles, semi-circles, triangles, rectangles, squares, trapezoids, hexagons, spheres, cubes, rectangular prisms, cones and cylinders. |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name |
Description |
| Which of These are Cubes? | Students are shown a set of three-dimensional figures and are asked to identify the cubes. In addition, they are asked to explain why the other figures are not cubes. |
| Turning a Square | Students are shown a square in various orientations and asked if it is still a square. |
| Spheres and Circles | Students determine if a globe and a circle are two-dimensional or three-dimensional and explain their reasoning. |
| Is it Still a Rectangle? | Students discuss the defining and non-defining attributes of rectangles. |
| Is it Plane or Solid? | Students examine a rectangle and a rectangular prism to discuss the similarities and differences. |
| Cubes and Prisms | Students compare a cube to a rectangular prism and discuss the similarities and differences. |
| Comparing a Cylinder to a Circle | Students compare the outline of the circular base of a cylinder to the cylinder itself. |
| Compare Hexagons | Students compare two hexagons and describe how they are alike and how they are different. |
Lesson Plans
| Name |
Description |
| Exploring Machine Learning to Train an AI Model | Students will explore Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) and pretrain a model to recognize and identify objects, including geometric shapes and aircraft. They will used unplugged activities to mimic sorting and classification of the objects using their prior knowledge and then make connections to human learning and Machine Learning. Students will then problem solve and propose solutions using an iterative process to improve the ML model to better recognize the objects. This lesson is an integrated Computer Science, Science and Math lesson designed for students in K-2 to apply math and science content knowledge while exploring and using computational thinking like people in Computer Science careers do. |
| Are You a Responsible Sorter and Citizen? | Students will identify and sort three-dimensional figures by their attributes while demonstrating and identifying qualities of responsible citizenship. |
| Understanding Polygons | This is a simple and fun activity that is great to incorporate into your geometry unit. As you read "The Greedy Triangle" aloud, the students "create" each shape with marshmallows and pretzel sticks - as you are reading the story, they complete a sheet in which they write the name of each shape, draw the shape, and record the number of sides and vertices each shape has. |
| Puzzled by Pattern Blocks! | In this lesson, the students will use two-dimensional pattern blocks to compose new shapes and fill in composite outlines of shapes. |
| Shape Identifying and Sketching | In this lesson students will describe attributes of triangles, rectangles, squares, and hexagons and identify these shapes by their attributes. Given the name of one of these shapes, students will use their knowledge of the shape's attributes to represent the shape with a sketch. |
| Being Shapely! | In this lesson, students will work collaboratively to identify and sketch shapes with defining and non-defining attributes. |
| Fun with Shapes | In this lesson students explore the composing of new shapes from other two-dimensional shapes. The students will utilize math benchmarks as they analyze math solutions and explain their solutions. Since the lesson uses composing, it is also a good lesson to use to show decomposing (taking a shape apart). |
Original Student Tutorials
| Name |
Description |
| Sorting Shapes | Learn to sort and identify two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes in this carnival-themed interactive tutorial. |
| Shape Sleuths: Rectangles and Squares | Help find clues to identify rectangles and squares and their defining attributes in this interactive tutorial. |
| Circus Fun: The Search for Circles | Learn the attributes, or characteristics, of a circle in this interactive tutorial. |
| The Search for Shapes: Exploring Hexagons | Help find hexagons based on their defining attributes for King Geo in this interactive tutorial. Learn what makes a hexagon a hexagon.
This is part of a series on the defining attributes of shapes. Click the links below.
|
| Shape Sleuths: Hexagons | Learn about the defining attributes of hexagons in this interactive tutorial series about shapes.
Click below to learn about other shapes.
|
| Shape Sleuths: Triangles | Learn about the defining attributes of triangles in this interactive tutorial series about shapes.
Click below to learn about other shapes.
|
Perspectives Video: Teaching Ideas
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
| Name |
Description |
| Sorting Shapes: | Learn to sort and identify two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes in this carnival-themed interactive tutorial. |
| Shape Sleuths: Rectangles and Squares: | Help find clues to identify rectangles and squares and their defining attributes in this interactive tutorial. |
| Circus Fun: The Search for Circles: | Learn the attributes, or characteristics, of a circle in this interactive tutorial. |
| The Search for Shapes: Exploring Hexagons: | Help find hexagons based on their defining attributes for King Geo in this interactive tutorial. Learn what makes a hexagon a hexagon.
This is part of a series on the defining attributes of shapes. Click the links below.
|
| Shape Sleuths: Hexagons: | Learn about the defining attributes of hexagons in this interactive tutorial series about shapes.
Click below to learn about other shapes.
|
| Shape Sleuths: Triangles: | Learn about the defining attributes of triangles in this interactive tutorial series about shapes.
Click below to learn about other shapes.
|