General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equal Sign
- Equation
- Expression
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to understand that the equal sign means “the same as.” In Kindergarten, students used objects or drawings to explain why addition or subtraction equations are true or false.- Instruction should include a variety of problem types where the sum or difference can be on either side of the equal sign. adding 2 and 4.
- Instruction may include the use of a balance with cubes to help students understand that the equal sign means the same as (MTR.2.1, MTR.6.1).
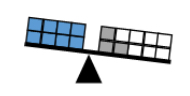
- For example, 8 = 3 + 5 is true because 8 is the result of adding 5 and 3.
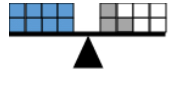
- For example, 8 = 2 + 4 is false because 8 is more than 6, which is the result of adding 2 and 4.
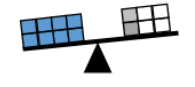
- For example, 8 = 3 + 7 is false because 8 is less than 10, which is the result of adding 3 and 7.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may not understand that the equal sign means “the same as,” since they may think the equal sign signals that the answer comes at the end. In these cases it can be beneficial to use a scale where students can complete problems to discover if in fact they are equal.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher provides number cards to build balanced equations.
- For example, using two sets of number cards 0 – 9, students build equations with two single digit addends on both sides.
- Alternatively, the teacher provides two of the missing addends and allows students to make the equation true using their number cards.

- Instruction provides opportunities to use a number balance to support understanding of the equal sign.
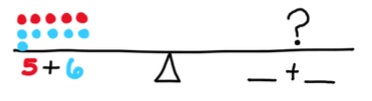
- For example, students build the expression 5 + 6 on one side of the balance and are asked to build an expression of equal magnitude of the other side. Students may choose to use a 9 and a 2, an 8 and a 3, or a 7 and a 4. Since students cannot use an 11 and must use two separate numbers instead, they are dispelling the misconception that the equal sign means “the answer is.”
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.3.1)
Lee had 14 building blocks. He then shared 6 of his blocks with his friend Remi. Create a true statement to show how many building blocks Lee has left.
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1)
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Tiffany says that 9 = 8 + 1 is a true statement. Paulie says it is a false statement. Who do you agree with Tiffany or Paulie? Why?
Instructional Item 2
What does the equal sign in 11 = 10 + 1 mean?
Instructional Item 3
Which of the following statements are true?a. 17 = 18 − 1b. 16 = 16 + 1c. 14 − 6 = 8d. 12 = 12e. 2 + 8 = 11
Instructional Item 4
Create a true statement where 19 is the sum.Instructional Item 5
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
