General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equation
- Expression
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to get students thinking about the relationships between addition and subtraction. In Kindergarten, students explored equations and developed an understanding of the equal sign by explaining why addition and subtraction equations are true using objects and drawings.- Instruction may present equations in different forms such as a + b = c or c = a + b.
- Instruction may include students using a related addition fact or a part-part-whole mat to help them find the missing addend in a subtraction equation.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may not recognize how an addition problem can help them solve a subtraction problem. Guided practice with related facts may be helpful for students who do not recognize this.
- Students may solve the equation and look for the solution in the answer choices rather than relying on reasoning.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
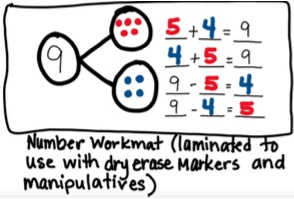
- Teacher provides opportunities to use number bonds to develop an understanding of fact families and inverse relationships.
- For example, students create a number bond for the number 9 using counters on a number bond work mat. Students then write the fact families for the number 9. Discussion should be focused on how the fact families are related and how knowing the addition facts can help the students solve a subtraction problem.
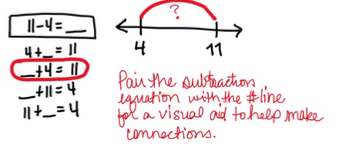
- Instruction provides opportunities to match a range of subtraction equations to their missing addend equation.
- For example, the teacher provides a variety of equations which may include: 11 – 4 = ____, 4 + ___ = 11, ___ + 4 = 11, ___ + 11 = 4, and 11 + ___ = 4. Students determine which missing addend equations will help them solve 11 – 4 = ____. The discussion should focus on reasoning about which missing addend equations will help them solve 11 – 4 = ____. The discussion should focus on reasoning about which equations will work and which will not.
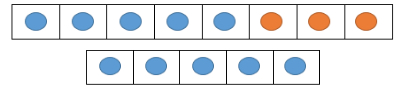
- Instruction provides opportunities to solve problems that highlight the relationship between addition and subtraction using a linear ten frame.
- For example, students use two different colors to shade the addend on the ten frame. Students write the addition fact that is represented on the ten frame 5 + 3 = 8. They then subtract 3 from 8 by folding under the three “orange” blocks. Students are left with the 5 “blue” blocks, so 8 − 3 = 5. They should practice with multiple addition facts. Discussion should be focused on the relationship between addition and subtraction.
- Teacher provides opportunities to work in reverse of the benchmark to solve missing addend equations and then write the subtraction equation that matches the missing addend equation.
- For example, students use two-color counters to build the knowns of the following equation on a given empty equation mat 5 + ____ = 9.
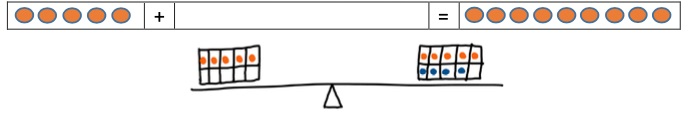
- Teacher asks “How many do you need to put in the empty space to equal the other side of the equation of you already have 5? Can we write a subtraction equation to help us solve this problem?”
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.7.1)
Katina has 14 grapes. She gives 8 of them to her brother Kevin. What addition problem could help Katina figure out how many grapes she has left for herself?
Instructional Items
Instruction Item 1
Which addition equation can help you determine 10 − 3?- a. 3+10=13
- b. 5+3=8
- c. 7+3=10
- d. 11+3=14
Instructional Item 2
Part A: Complete the part-part-whole mat to help you determine 11 − 5.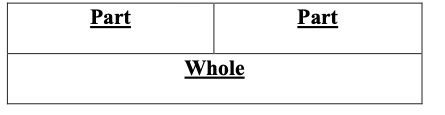
Part B: Write an addition equation that could help you solve.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.