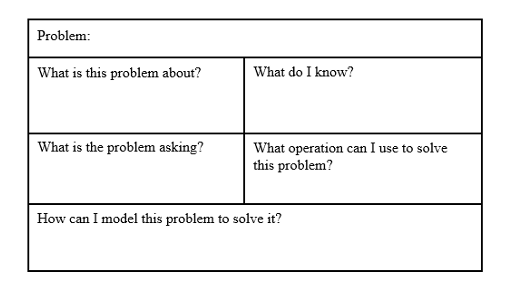
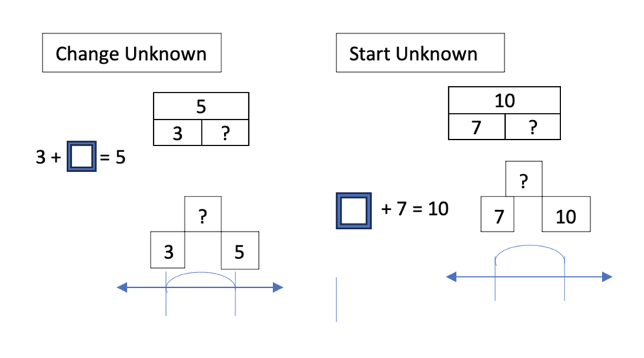
Solve addition and subtraction real-world problems using objects, drawings or equations to represent the problem.
Instruction includes understanding the context of the problem, as well as the quantities within the problem.
Addition and subtraction are limited to sums within 20 and related subtraction facts. Refer to
.
| Name |
Description |
| Turtles in a Pond | Students are given pairs of word problems that can be solved using the Commutative Property of addition. |
| Take From (Result Unknown) | Students are asked to solve two Take From (Result Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Add To (Change Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Add To (Change Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Take From (Start Unknown) | Students are asked to solve two Take From (Start Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Compare (Smaller Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Compare (Smaller Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| How Many M&M's? | Students are asked to solve two Compare problems presented using the terms more than and fewer than. |
| How Many More Stickers? | Students are asked to solve a Compare (Difference Unknown) word problem using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Compare (Difference Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Compare (Difference Unknown) word problems within 20 using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Compare (Bigger Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Compare (Bigger Unknown) problems presented using the terms more than and fewer than. |
| Both Addends Unknown | Students are asked to solve a Put Together/Take Apart (Both Addends Unknown) word problem and explain their strategies. |
| Trains and Jump Ropes | Students are asked to solve two Compare problems presented using the terms more than and fewer than. |
| The Cupcake Problem | Students are asked to solve two Take From (Start Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Take From (Change Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Take From (Change Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Red Birds and Blue Birds | Students are asked to solve two Put Together/Take Apart (Addend Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Put Together/Take Apart (Total Unknown) | Students are asked to solve two Put Together/Take Apart (Total Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Put Together/Take Apart (Both Addends Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve a Put Together/Take Apart (Both Addends Unknown) word problem using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Put Together/Take Apart (Addend Unknown) Word Problem | Students are asked to solve two Put Together/Take Apart (Addend Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| More Add To (Change Unknown) Problems | Students are asked to solve two Add To (Change Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Add To (Start Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Add To (Start Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Add To (Result Unknown) Word Problems | Students are asked to solve two Add To (Result Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Fish in a Pond | Students solve a Take From (Start Unknown) word problem. |
| Birds on a Branch | Students are asked to solve two Take From (Change Unknown) word problems using pencil and paper or other appropriate manipulatives. |
| Name |
Description |
| The Whole Part | Students will participate in a variety of activities and use part-part-whole graphic organizers to discover unknown addends in put together addition situations. |
| Pete's Groovy Button Problems | This lesson uses a familiar character, Pete the Cat, that proposes a comparison problem for students to explore. |
| Addition Stories at the Food Store | In this lesson, students will solve addition whole number word problems (within 20) with real-world scenarios by using manipulatives, drawings, or equations. |
| Cookie Subtraction | In this lesson, the teacher shares the book, "Mmm... Cookie Simple Subtraction". The students follow along by representing the problems in the book with cookie manipulatives and recording the equations for each problem. The lesson incorporates a variety of subtraction problem types. |
| Get Up and Go! with Addition and Subtraction | The lesson involves students adding and subtracting on a number line while follwoing a story that explains the amount of time taken to get ready in the morning. Students will write addition and subtraction equations to represent the parts of the story. |
| What's Missing? | In this lesson, students learn to solve addition equations that have a missing addend within 10. |
| Word Problem Lesson | In this lesson, students will be able to solve "compare" word problems. |
| Solving Word Problems Using Story Structure | In this lesson, students will learn how to use their knowledge of beginning, middle, and end to solve word problems that include result unknown, change unknown, and start unknown. They will learn how to use a modified story map to write an equation to represent the problem. |
| Dangerous Doubles (Doubling Numbers) | This lesson teaches students to use the strategy doubling numbers and doubles plus or minus one in order to use mental math to add one-digit numbers. The students are engaged in learning through the read-aloud of "Double the Ducks" by Stephen Murphy and then get to work with a partner to draw doubles and write equations that relate to their drawings. Students individually work on solving word problems using these strategies and manipulatives as necessary to solve. |
| Rock Around the Clock | In this lesson, students will use addition or subtraction strategies to solve a real-world problem about developing a music playlist. |
| Name |
Description |
| Finding a Chair | These problems explicitly describe one-to-one correspondences without using comparison language. Such problems are easier for students to solve than problems that use comparison language such as "How many more?" or "How many fewer." |
| Field Day Scarcity | The purpose of this task is for students to relate addition and subtraction problems to money in a context that introduces the concept of scarcity. Scarcity occurs when you want or need more than you can have. Students may want to buy everything but will discover that it not possible with only $7 and they will have to make decisions. |
| Boys and Girls, Variation 1 | Students may use either addition or subtraction to solve these types of word problems, with addition related to the action of putting together and subtraction related to the action of taking apart. Depending on how students think about these word problems, either is appropriate for the "addend unknown" problems. Seeing it both ways emphasizes the relationship between addition and subtraction. |
| At the Park | This task includes three different problem types using the "Add To" context with a discrete quantity. |
| Maria’s Marbles | Students benefit from encountering one problem type limited to small numbers and to develop strategies for that type of problem before encountering mixed sets of problems and larger numbers that distract the student from the problem itself. Over time they will be able to distinguish between types of problems in mixed sets and apply the appropriate strategy to solve each. |
| The Pet Snake | The purpose of this task is for students to gain a better understanding of measurements with the example being the growth of a pet snake. |
| Sharing Markers | These task types represent the Take From contexts for addition and subtraction. This task includes the three different problem types using the Take From context: result unknown, change unknown, and start unknown. Students need experience and practice with all three types. |
| Name |
Description |
| Finding a Chair: | These problems explicitly describe one-to-one correspondences without using comparison language. Such problems are easier for students to solve than problems that use comparison language such as "How many more?" or "How many fewer." |
| Boys and Girls, Variation 1: | Students may use either addition or subtraction to solve these types of word problems, with addition related to the action of putting together and subtraction related to the action of taking apart. Depending on how students think about these word problems, either is appropriate for the "addend unknown" problems. Seeing it both ways emphasizes the relationship between addition and subtraction. |
| At the Park: | This task includes three different problem types using the "Add To" context with a discrete quantity. |
| Maria’s Marbles: | Students benefit from encountering one problem type limited to small numbers and to develop strategies for that type of problem before encountering mixed sets of problems and larger numbers that distract the student from the problem itself. Over time they will be able to distinguish between types of problems in mixed sets and apply the appropriate strategy to solve each. |
| The Pet Snake: | The purpose of this task is for students to gain a better understanding of measurements with the example being the growth of a pet snake. |
| Sharing Markers: | These task types represent the Take From contexts for addition and subtraction. This task includes the three different problem types using the Take From context: result unknown, change unknown, and start unknown. Students need experience and practice with all three types. |
| Name |
Description |
| Finding a Chair: | These problems explicitly describe one-to-one correspondences without using comparison language. Such problems are easier for students to solve than problems that use comparison language such as "How many more?" or "How many fewer." |
| Field Day Scarcity: | The purpose of this task is for students to relate addition and subtraction problems to money in a context that introduces the concept of scarcity. Scarcity occurs when you want or need more than you can have. Students may want to buy everything but will discover that it not possible with only $7 and they will have to make decisions. |
| Boys and Girls, Variation 1: | Students may use either addition or subtraction to solve these types of word problems, with addition related to the action of putting together and subtraction related to the action of taking apart. Depending on how students think about these word problems, either is appropriate for the "addend unknown" problems. Seeing it both ways emphasizes the relationship between addition and subtraction. |
| At the Park: | This task includes three different problem types using the "Add To" context with a discrete quantity. |
| Maria’s Marbles: | Students benefit from encountering one problem type limited to small numbers and to develop strategies for that type of problem before encountering mixed sets of problems and larger numbers that distract the student from the problem itself. Over time they will be able to distinguish between types of problems in mixed sets and apply the appropriate strategy to solve each. |
| The Pet Snake: | The purpose of this task is for students to gain a better understanding of measurements with the example being the growth of a pet snake. |
| Sharing Markers: | These task types represent the Take From contexts for addition and subtraction. This task includes the three different problem types using the Take From context: result unknown, change unknown, and start unknown. Students need experience and practice with all three types. |