General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Cardinality Principle
- Natural Number
- Number line
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to understand that the value of a digit is impacted by its position in a number. A three in the tens place has a value of 30 while a 3 in the ones place has a value of 3. In Kindergarten, students located, ordered and compared numbers from 0 to 20 using the same number line. Students fill in missing numbers on a number a line. Kindergarten students are not expected to use the relational symbols =, > or < when comparing numbers (MTR.5.1).- Instruction may include students modeling the numbers with manipulatives to compare given numbers prior to placing them on the number line or after placing them on a number line.
- Instruction may include students’ writing numbers in expanded form to compare given numbers.
- Instruction may include students plotting numbers on number lines to compare numbers.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may not recognize that a number’s value is directly related to its placement on a number line. In these cases, having students build a number using base ten manipulatives prior to plotting the number onto a number lines could be helpful.
- Students may not understand the digit in the greatest place helps determine the correct comparison unless it is equal. For example: 29 is less than 31 even though there is a 9 in the number 29. Building these numbers with base ten blocks or place value disks might be helpful.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher co-constructs a number line (string or painter’s tape), labeling the ends of the
number line (0-100). Students are asked to place 50 on the number line. Teacher
discusses the placement of the number and then repeat the process with the numbers 25
and 75. Teacher asks students to identify numbers that are greater than... and less than....
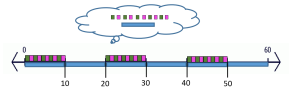
- Example: Teacher provides opportunities to use a number line and place value chart with base-ten blocks. Have students begin by placing the place value rods end to end along the number line (creating a number path). If students have difficulty with understanding that each rod represents a group of ten, use tiles or units to represent each whole number on the number line (number path).
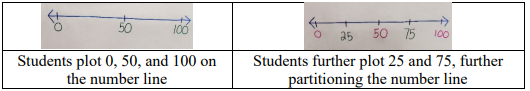
- Teacher asks students to plot and represent a number on the number
line and on the place value chart. Then, the teacher asks students to identify a number that
is greater, also plotting this number on the number line and representing the number on
the place value chart. Repeat with a number that is less than.
- Example:
- Teacher provides opportunities to allow students to use a place value chart with base ten blocks or place value discs to build numbers and compare. Have students build each number using a place value chart. Then, model the thinking of looking at the tens place when starting to compare the numbers. If the digit is the same, then have students move on to comparing the ones place.
- For example, give students two two-digit numbers to compare like 34 and 43. Have students represent both numbers in the place value chart. Teacher asks, “How many tens does each number have?”, “Which number has more tens?” Students should be able to state that 43 is greater than 34 since it has one more ten than 34. Repeat this with numbers that have the same digit in the tens place and how the ones place would be used to determine the correct comparison.
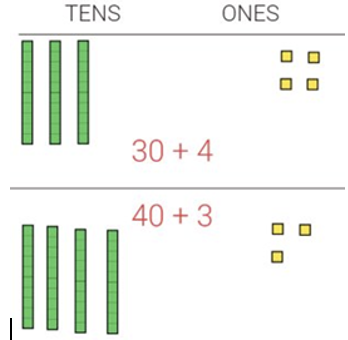
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.1.1, MTR.2.1 ,MTR.4.1, MTR.5.1)
Class Plotting on an Open Number LineMaterials: 4 Clothespins, 4 index cards, 4 feet of string or rope
Teacher: Hang a piece of string in the front of the classroom.
- Ask a student to think of a two digit number that has 3 tens in it. Write that number on an index card. Ask another student to place the number anywhere on the piece of string (open number line) using a clothespin.
- Ask a student to think of a two digit number that has 5 tens in it. Write that number on an index card. Ask another student to place the number on the piece of string (open number line) using a clothespin. Ask the class if it should be placed to the right or the left of the first number. Ask “Is this number more or less than our first number?”
- Ask a student to think of a two digit number that has 9 ones in it that would come after the 5 tens number. Write that number on an index card. Ask another student to place the number on the piece of string using a clothespin. Ask the class if it is greater than, less than, or equal to the first number on the number line. Ask the class if adjustments are needed to make room for the new number on the open number line (string). Make adjustments as needed.
- Ask a student to think of a number that would come between the first and second number. Write that number on an index card. Ask the class “Should this number be placed closer to the first number or second number? How do you know?” Ask the class if adjustments are needed to the number line more accurate now that they have all the numbers placed. Make adjustments as needed.
- Ask students to independently come up with at least three different true statements from the numbers on the class number line using >, < or = symbols. After giving students time to come up with statements, call on students and write their findings and ask students to evaluate if they are in fact true statements. Remind students to come up with both greater than and less than statements.
Sample Class Number Line:
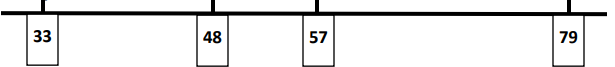
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.1.1, MTR.2.1 , MTR.4.1, MTR.5.1)
Teacher provides 6 to 10 numbers on cards in either standard form, expanded form, word form or pictural form. Ask students to place them in ascending order. If any numbers are equal, they can be placed on top of each other to show that they are located at the same spot because they represent the same number. Ask students to come up with at least five different true statements from the numbers using the <,>, or = symbols.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Order the numbers 99, 79 and 89 from least to greatest. Plot the numbers on the number line.
Instructional Item 2
Using the numbers 99, 79 or 89, make three true statements.
Instructional Item 3
Write a true statement using the numbers 63 and 36.*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
