General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- NA
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to develop a foundation for statistical thinking, as well as providing a context to support the development of counting skills (MTR.5.1).In grade 1, students will organize data using tally marks or pictographs and compare categories by counting the objects in each category.- Instruction reinforces the counting and comparing benchmarks within the Number Sense and Operations strand (MTR.5.1).
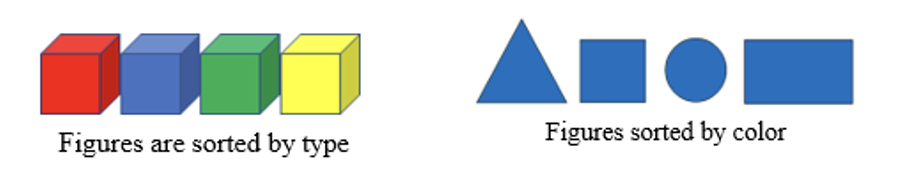
- Instruction reinforces the identifying and sorting of figures benchmarks within the Geometric Reasoning strand (MTR.5.1).
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may not clearly define categories for sorting objects which may lead to inaccurate data collection as objects fit into multiple categories.
- When students are presented with objects to be sorted into predefined categories, they may be frustrated that some objects don’t fit into any category.
- Students may misrepresent the count for each category.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes opportunities for students to sort objects by given attributes.
- For example, have students sort themselves into categories based on transportation to school (bus rider, car rider, extended day, walker). Students can report their sorting using drawings or numerals.
- For example, provide students crayons and ask students to sort crayons by color. Students will sort the crayons into 4 categories: red, blue, green, and yellow. Possible questions to ask during this activity:
- How many red crayons are there?
- How many green crayons are there?
- Which category has the most crayons?
- Which category has the least crayons?
- How many more blue crayons are there than yellow crayons?
- Instruction includes opportunities to sort two-dimensional and three-dimensional geometric figures by attributes. For example, teacher places foam, wood and/or pattern blocks into a bucket. Students are asked to sort the figures. The teacher will see how students sort the figures and ask the students to explain why they sorted the figures a particular way (could be by color, size, texture etc.) If students are unsure of where to place a figure, help students determine what category in which to place the figure by having a discussion on the attributes of the figure in relationship to the attributes of the sorted figures. Students will count how many figures are in each of their categories and record the numeral. The teacher asks comparing questions about the groups such as:
- “How are these shapes different from one another?”
- “Are there more red shapes or blue shapes?”
- “Are there more squares than triangles?”
- The teacher will then ask the students to sort the figures another way and repeat the activity after the figures have been classified a new way.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1(MTR.5.1)
Provide students with cards or objects that can be sorted multiple ways (i.e., shapes that are various colors and could be sorted by shape or color). In a group, give students time to think and discuss the various ways the cards or objects can be sorted. After a discussion, the group will decide a way to sort the cards or objects and do so. Then the teacher asks questions such as:
- “Which category has the most?”
- “Which category has the least?”
- “How many are in [fill in the blank] category”?
After a discussion, the cards or objects can be sorted using a different attribute and the task can begin again.
Instructional Task 2(MTR.3.1)
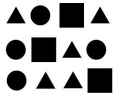
Ask students to sort the figures into groups of circles, rectangles and triangles.
- Which shape appears the most?
- How many more triangles are there than circles?
- How many squares are there?
- How many figures have straight sides?
Instructional Task 3(MTR.1.1, MTR.7.1)
- Which favorite food had the greatest number of votes?
- Which favorite food has the least number of votes?
- Are there any favorite foods with the same number of votes?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
- Part A: Sort the data.
- Part B: Report the data with drawings.
Instructional Item 2
Part A. Circle the buttons that are shaped like triangles. Part B. How many buttons are shaped like a triangle?
Instructional Item 3
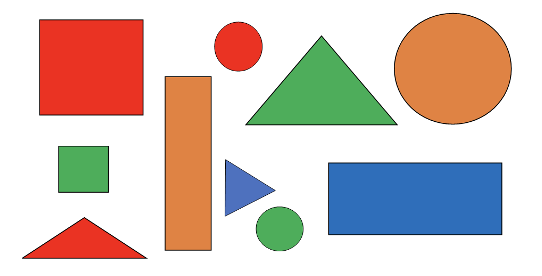
Part A: Sort the figures by color.
Part B: How many figures are green?
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive
