
|
Generated on 7/31/2025 at 3:34 AM |
The webpage this document was printed/exported from can be found at the following URL:
https://www.cpalms.org//PreviewStandard/Preview/15247
https://www.cpalms.org//PreviewStandard/Preview/15247
Express the length of an object, up to 20 units long, as a whole number of lengths by laying non-standard objects end to end with no gaps or overlaps.
Standard #: MA.K.M.1.3
Standard Information
Standard Examples
Example: A piece of paper can be measured using paper clips.
Standard Clarifications
Clarification 1: Non-standard units of measurement are units that are not typically used, such as paper clips or colored tiles. To measure with non-standard units, students lay multiple copies of the same object end to end with no gaps or overlaps. The length is shown by the number of objects needed.
General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: K
Strand: Measurement
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Standard Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- NA
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to develop the foundation for measuring with given units. Though students will take measurements using non-standard units or objects, this will provide a foundation for standard units of measurement in later grades (MTR.5.1).- Instruction emphasizes the naming of units when recording or giving measurements.
- For example, the pencil is 6 paperclips long.
- Instruction uses objects that can be measured in whole units, or close enough that there will be no misconceptions or errors related to rounding or estimating.
- Instruction includes concrete objects as well as images and context for students to measure (MTR.7.1).
- Instruction includes students measuring an object using various non-standard units (erasers, paperclips or candy bars), comparing the results and seeing that when the unit is larger the number required is smaller (MTR.2.1).
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may leave gaps or overlaps between objects when measuring, leading to inaccurate results.
- Students may mix different size units in the same measurement.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
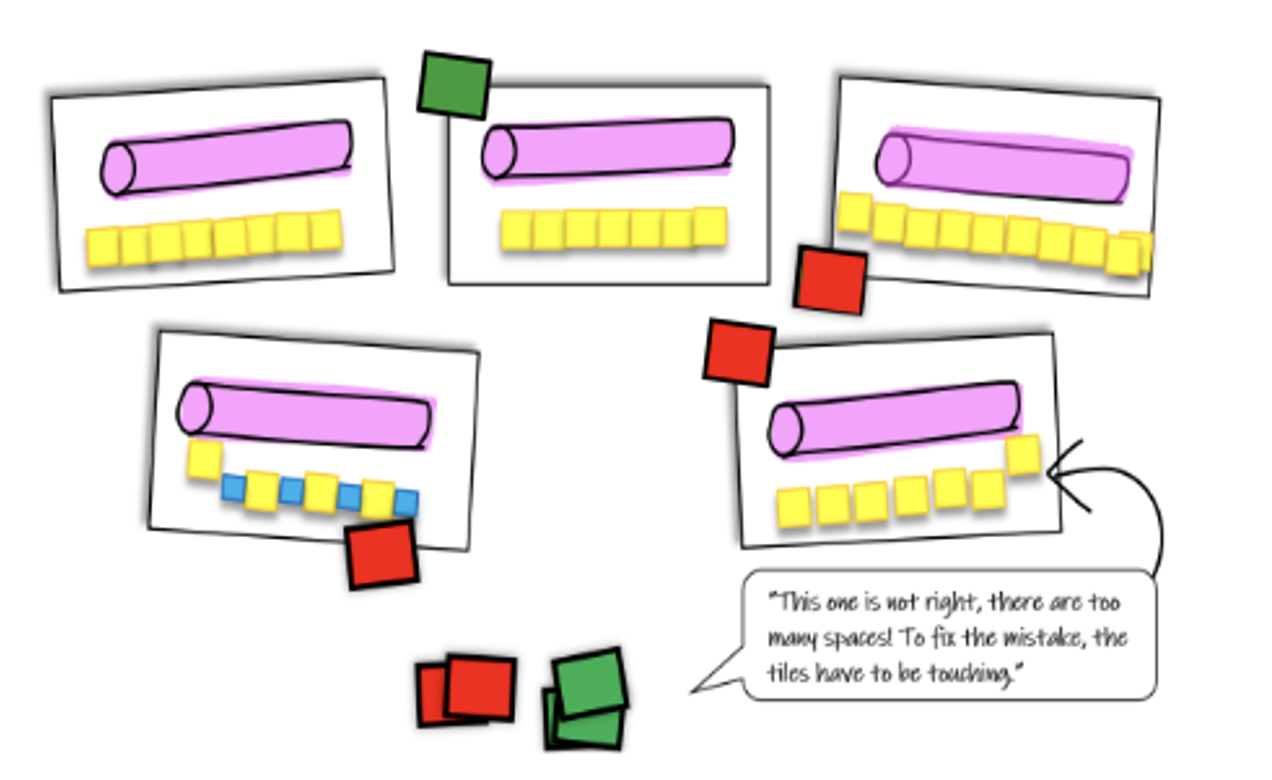
- Instruction includes discussions about measurement during activities or tasks and should emphasize to students the idea that units of measure must be equal in length and size; and that each length unit must be touching the next. Tasks can include presenting students with identical objects that show a length of measure, some of which are incorrectly measured. Encourage students to evaluate and verbalize their thinking to justify why or how each object is measured correctly or not.
- For example, images or pictures can be shown to students that include both examples and non-examples of the same object, such as a straw, that has been measured. Students can justify their thinking about how the object was measured, label each image with a “yes (green)” or a “no (red),” and then tell how to fix the mistake
- Teacher models using one-inch grid paper cut into strips to place next to or below an object when measuring. One-inch square tiles are then placed on the grid paper strip to be used as a guide to place each unit precisely, with no gaps or overlaps. As students find success with tile placement, the grid paper strip can be used next to or below the placement of the tiles, until it is no longer needed.
- Example:
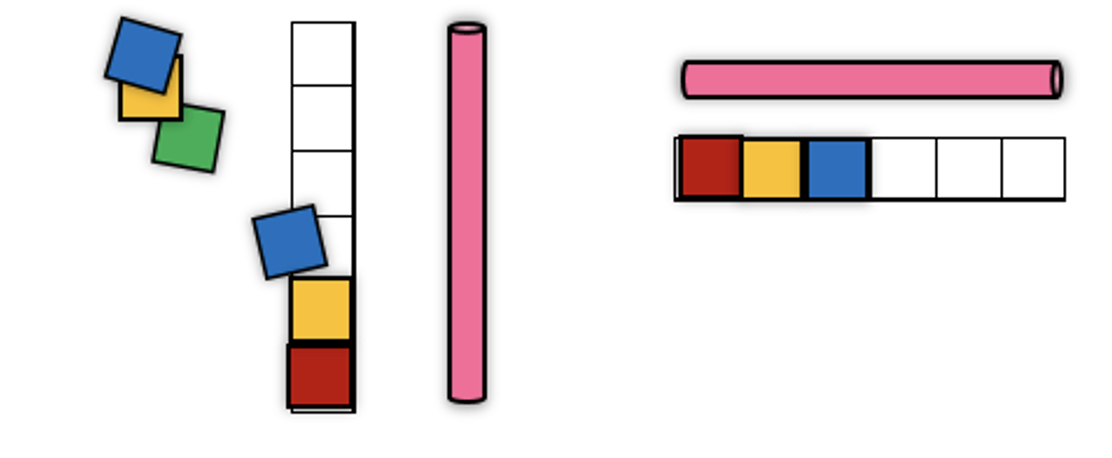
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1(MTR.2.1)
You will need objects to use as a unit of measurement (paperclips, tiles or other non-standard units) and various items to measure. In a group, have students pick which unit they will use to measure the objects with. (It is okay if students have different objects to measure with, but should all measure the same item.) Students will measure and report their findings to the group. The teacher will lead a discussion around their findings and compare responses.
The ____________________ is ______ paper clips long, but it is ______ color tiles long.
The group can discuss why they had different results even though they measured the same item. (The paperclip is shorter than the tile, so more paper clips are needed than tiles.). After the discussion, repeat the task. Students can be encouraged to make predictions based on the previous discussion.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
How many paper clips long is the pencil?

*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
Related Courses
- Grade Kindergarten Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) # 5012020
- Access Mathematics - Grade Kindergarten (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) # 7712015
- Foundational Skills in Mathematics K-2 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) # 5012005
Related Access Points
- MA.K.M.1.AP.3 # Express the length of an object, up to 10 units long, as a whole number of lengths using non-standard objects laid end to end with no gaps or overlaps.
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
- Using Tiles to Measure # Students use color tiles to measure the lengths of two figures shown on the accompanying worksheet.
- Using Paper Clips to Measure # Students use paper clips to measure the length of two pictured items.
- Using Cubes to Measure Height # Students determine their heights determined by cutting a length of string to show this measurement. Then using snap cubes they measure the length of the string. Note: The measurement of the string will extend past 20 units, use this task with students who demonstrate a readiness to go beyond the measurement of 20 units.
- Measuring the Width and Height of a Book # Students are asked to use cubes to determine the length of different sized edges of a book.
- Measure With Paper Clips # Students measure the length of an unsharpened pencil with paper clips.
- Measure With Color Tiles # Students use color tiles to measure the length of rectangles.
Lesson Plans
- Measuring End to End is a Win-Win! # Be a winner at measuring length by learning how to measure from end to end! Students will learn where the first end and the last end are on an object. They will learn about lining up multiple copies of a non-standard measurement unit, with no gaps or overlaps, from end to end along the length of the object being measured and expressing the object’s length as the number of non-standard measurement units needed.
- Measuring Madness # After sharing the story Measuring Penny by Loreen Leedy, students will be excited to learn how to measure with nonstandard measuring tools. Your students will want to measure everything in the classroom!
- Spring Festival Flower # In this MEA, students will help pick a flower that will be the focus of the Spring Festival. They will practice counting pictures and representing the number of pictures with a written numeral.
- Totally Wholly Lengths # In this lesson students will measure the lengths of various objects by placing inch- or centimeter-length manipulatives end-to-end without gaps or overlaps and counting them.
- "How Long is Your Train?" # This lesson is intended to allow students to gain insight into the importance of measurement. The focus is on using non-standard units to measure the length of a "train" they create. Students are then required to compare the length of their train with a buddy's train.
- Around the Room Measuring # In this lesson, students practice measuring length using non-standard units of measurement.
- Measuring with Inchworms # Students will measure the length of objects using non-standard units and report the length shown by the number of non-standard objects needed. Students will explore laying non-standard units end to end with no gaps and overlaps. Students will listen to the book Inch by Inch.
- Fishy Lengths - Which fish is right for my aquarium? # Students explore lengths of fish to determine if fish are too long to fit in different sized aquariums. Students will use non-standard units and measuring tools to compare the lengths of fish and boxes without being able to directly hold the fish near the boxes.
-
Beach Measurements # The students will read about characters competing in a contest at the beach. The characters use some very creative ways to measure the lengths of their sandcastles, moats, and walls. Students will use non-standard units to measure the lengths of various beach objects. A fun and engaging lesson on non-standard measurement.
- How Big is a Dinosaur? # In this dinosaur-themed lesson, students will use dinosaur manipulatives (and the teacher will demonstrate using a longer dinosaur footprint print-out) as units for nonstandard measurement of length. Students will use length comparison statements.
Original Student Tutorial
- Picnic Lunch by the Length – Measuring Horizontal Lengths Using Non-Standard Objects # Help Willow and Sam measure how long objects are by counting how many copies of a shorter object fit from one end of the object to the other without any gaps or overlaps in this picnic-themed, interactive tutorial.
Problem-Solving Tasks
- Measure Me! # The purpose of this task is for students to measure something that interests them (namely themselves) by laying multiple copies of a shorter object that represents the length unit end to end. This task provides students an opportunity to discuss the need to be careful when measuring as it is very likely that some of them will get incorrect comparisons of their leg length with their partner's leg length.
- How Long # The purpose of this task is to help students learn how to take measurements.
- Measuring Blocks # In this task, students work in pairs to measure a block using paperclips.
Tutorial
- Measuring Length With No Gaps or Overlaps # In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, called, "Measuring a golden statue", we see an example of how to solve a problem in which we measure an object with same-size length units that span it with no gaps or overlaps.
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
- Spring Festival Flower # In this MEA, students will help pick a flower that will be the focus of the Spring Festival. They will practice counting pictures and representing the number of pictures with a written numeral.
MFAS Formative Assessments
- Measure With Color Tiles # Students use color tiles to measure the length of rectangles.
- Measure With Paper Clips # Students measure the length of an unsharpened pencil with paper clips.
- Measuring the Width and Height of a Book # Students are asked to use cubes to determine the length of different sized edges of a book.
- Using Cubes to Measure Height # Students determine their heights determined by cutting a length of string to show this measurement. Then using snap cubes they measure the length of the string. Note: The measurement of the string will extend past 20 units, use this task with students who demonstrate a readiness to go beyond the measurement of 20 units.
- Using Paper Clips to Measure # Students use paper clips to measure the length of two pictured items.
- Using Tiles to Measure # Students use color tiles to measure the lengths of two figures shown on the accompanying worksheet.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades K-5
- Picnic Lunch by the Length – Measuring Horizontal Lengths Using Non-Standard Objects # Help Willow and Sam measure how long objects are by counting how many copies of a shorter object fit from one end of the object to the other without any gaps or overlaps in this picnic-themed, interactive tutorial.