General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equal sign
- Equation
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to allow students to continue to flexibly discover various sums as they work towards procedural reliability in Kindergarten, and automaticity in grade 1. This benchmark allows students the opportunity to deepen understanding of addition and subtraction by connecting the concepts to real-world situations. Though this should not be the first exposure to contextual addition and subtraction problems, this benchmark provides the opportunity for making it explicit (MTR.7.1).- Instruction includes the relationship between addition and subtraction, providing opportunities for discovering subtraction facts that are related to addition facts (MTR.5.1).
- Instruction includes opportunities for the use of various strategies and for students to collaborate and share strategies with each other (MTR.2.1, MTR.4.1).
- Items or explanations including equations as strategies may help students begin to understand the meaning of the equal sign.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
Students may not yet have an understanding of the equal sign when attempting to use equations as a strategy (see MA.K.AR.2.1).
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Teacher provides a graphic organizer to identify important information for solving the problem.
- For example, students develop an understanding of context and reasoning by answering questions about the context and gathering information from the problem to promote reasoning.
- Instruction provides opportunities to determine the context of numberless word problems with a focus on what is happening in the problem and how to solve it.
- For example, the teacher provides the following word problem to students.
- Daniella has ____ marbles and Shelby has ____ marbles. How many marbles do they have altogether?
- Teacher asks: What is this problem about? What is happening in this problem? What information do we know? How do you think you would solve this problem?
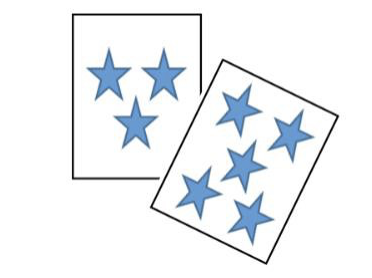
- Instruction includes opportunities to write an equation given sets of pictures or manipulatives. Alternatively, students can work in reverse, pull a card from the stack that represents the sum and generate as many equations as possible to match the sum.
- For example, students are given a set of cards, and they write an equation to represent the quantity of objects on the cards and their sum. In this case, 3 + 5 = 8.
- Teacher models with manipulatives to represent equations.
- For example, the teacher models an equation, then gives students two-color counters or snap cubes to use to represent equations. Given the equation 4 + 2 = 6, students build a set of four and a set of two and then count to determine the sum.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.7.1)
- Dani and Ciara colored 9 pages of a coloring book altogether. How many pages could Dani and Ciara each have colored. Use manipulatives, drawings, or equations to explain your thinking.
Enrichment Task 1 (MTR.2.1)
- Using Instructional Task 1, have students represent multiple solutions.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
- Stan found 7 marbles cleaning his room. He found 3 marbles in the kitchen. How many marbles does Stan have?
Instructional Item 2
- Eddie has 10 tokens saved for a class prize. He spent 8 tokens to get a prize from the class treasure box. How many tokens does Eddie have left?
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
