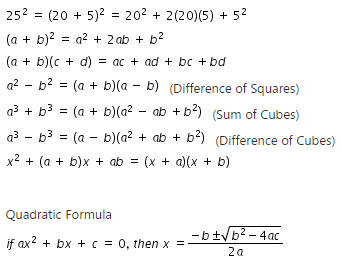
Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Create/identify identities with numbers (e.g., 4 + 0 = 4).
- Match a and b with their value using a tool (e.g., transparency overlay).
- Model the equation using manipulatives (e.g., algebra tiles).
- Match terms in the identity with their value.
- Match an equation with its polynomial identity.
- Substitute numbers/variables into the identity to generate equations.
- Understand the following concepts and vocabulary: property, identity, polynomial, factor, expand, substitution.
| Number: MAFS.912.A-APR.3.AP.4a | Category: Access Points |
| Date Adopted or Revised: 06/14 |
Cluster:
Use polynomial identities to solve problems. (Algebra 2 - Additional Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |
