Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Add and subtract integers (e.g., use manipulatives, a number line or calculator to add 2 + -5).
- Use manipulatives to demonstrate what an exponent represents
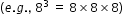 .
. - Produce the correct amount of base numbers to be multiplied given a graphic organizer or template.
- Use manipulatives to simplify expressions using properties of exponents. (such as power of a power, product of powers, power of a product, and rational exponents, etc.).
- Use manipulatives to demonstrate exponential decay or growth. (i.e., Given a cup of M&M’s, pour them on a plate and remove the M&M’s with the M side up. Collect the remaining M&M’s and put in cup and repeat until there is only 1 M&M left. Record data and graph at each step.)
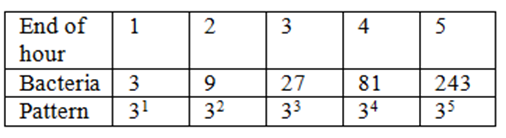
- Given a table, identify whether a function is growing exponentially.
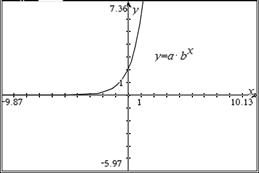
- Given an equation, identify whether it is an exponential function.
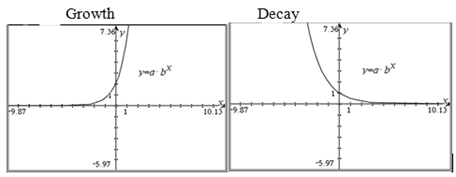
- Identify whether an exponential function is a growth function or a decay function based on its graph.
- Understand the following concepts, symbols, and vocabulary: base number, exponent, integer.
- Select the correct expanded form of what an exponent represents
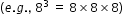 .
. - Identify the number of times the base number will be multiplied based on the exponent.
- Understand that a negative exponent will result in a fraction with a numerator of 1
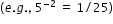 .
. - Understand that b determines whether the graph will be increasing (growth) or decreasing (decay).
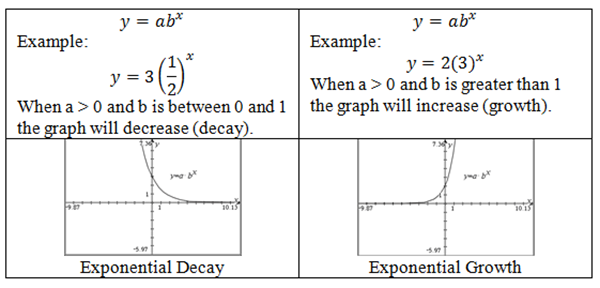
- Understand that b can be written as (1+r) or (1-r) where r is the rate of change.
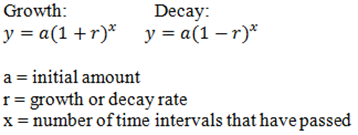
- Teacher Tool: Click Here
| Number: MAFS.912.A-SSE.2.AP.3e | Category: Access Points |
| Date Adopted or Revised: 07/14 |
Cluster:
Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems. (Algebra 1 - Supporting Cluster) (Algebra 2 - Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |

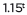 can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as 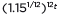 ≈
≈ 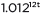 to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%.
to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%.