Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Identify a composite three-dimensional (3-D) figure (i.e., two or more rectangular prisms put together).
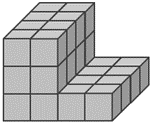
- Decompose the composite figure into two separate rectangular prisms.
- Pack each rectangular prism with unit cubes.
- Find the volume of figure a (e.g., by counting all of the unit cubes); find the volume of figure b; add the two volumes together.
- Understand the following vocabulary and concepts: volume, composite 3-D figure, decompose, rectangular prism, length, width, height.
- Use a visual representation of a composite figure to determine the total volume of figure a and figure b combined.
| Number: MAFS.5.MD.3.AP.5b | Category: Access Points |
|
Cluster:
Geometric measurement: understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition. (Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |
