Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.
Remarks
Examples of Opportunities for In-Depth FocusThe extension of the place value system from whole numbers to decimals is a major intellectual accomplishment involving understanding and skill with base-ten units and fractions.
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
- Assessment Limits :
Items may require a comparison of the values of digits across multiple place values, including whole numbers and decimals from millions to thousandths. - Calculator :
No
- Context :
Allowable
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
What is the missing value in the equation shown?
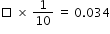
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
What is the value of the missing number in the following equation?
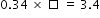
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 3
- Question:
How many times the value of 0.034 is the value of 0.34?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 4
- Question:
Which statements about the values 0.034 and 3.40 are true?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MS: Multiselect
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
ResourceID: 49826
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
A fire caused by faulty wiring set off a sprinkler system, which damaged a school. The school must be remodeled and the electrical wiring must be replaced. Students will decide which materials to use to as conductors and which to use as insulators in the new wiring.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students are asked to find  of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.
of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.
Given an odometer reading, students are asked to discuss the value of each digit and explain how a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as the same digit to its right, and one-tenth as much as the same digit to its left.
Students are presented with two decimals in the context of a distance word problem and asked to tell how many times longer one distance is than the other.




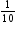 of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.
of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.

