Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
- Assessment Limits :
Quotients in division items may not be equivalent to a whole number. Items may contain fractions greater than 1. Items may not use the terms “simplify” or “lowest terms.” Only use whole numbers for the divisor and dividend of a fraction. For given fractions in items, denominators are limited to 1-20. - Calculator :
No
- Context :
Allowable
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
Which expression is equivalent to
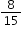 ?
? - Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question:
Joe has a board that is 6 feet long. He needs to cut the board into 15 equal-length pieces.
How many feet long should each piece of the board be?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 3
- Question:
An art teacher gives a total of 35 pounds of clay to her students. She gives each of her 16 students the same amount of clay.
How many pounds of clay does each student get?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Educational Game
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorials
Problem-Solving Tasks
Teaching Idea
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
The Birds Now Pet Store is increasing the size of its bird department. By increasing the number and types of birds, they need to purchase more bird food and the type of food needs to be one that different types of birds can eat. The students need to rank the companies that sell bird food base on the basic requirements out lined in the client's letter.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
Students use mathematical practices to recommend food packages for the Wildlife Refuge of North America to order.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students are asked to interpret an improper fraction and then write a word problem to match the context of the fraction.
Students are asked to draw a visual fraction model to solve a division word problem.
Students are asked to draw a visual fraction model to solve a division word problem.
Students are asked to interpret a fraction and write a word problem to match the context of the fraction.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades K-5
Learn to identify a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator using fraction models in this interactive tutorial.
Help Buffy multiply fractions by whole numbers using the standard algorithm in addition to visual fraction models in this bakery-themed, interactive tutorial.
This is part 4 of a 4-part series. Click below to open other tutorials in the series.
Computer Science Original Student Tutorials
Learn how to define, declare and initialize variables as you start the journey to "bee" a coder in this interactive tutorial. Variables are structures used by computer programs to store information. You'll use your math skills to represent a fraction as a decimal to be stored in a variable.
This is part 1 of a 4-part series on coding. Click below to open the other tutorials in the series.
- Bee A Coder Part 2: Condition Statements
- Bee A Coder Part 3: If Statements
- Bee A Coder Part 4: Repeat Loops
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
Help Buffy multiply fractions by whole numbers using the standard algorithm in addition to visual fraction models in this bakery-themed, interactive tutorial.
This is part 4 of a 4-part series. Click below to open other tutorials in the series.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Learn how to define, declare and initialize variables as you start the journey to "bee" a coder in this interactive tutorial. Variables are structures used by computer programs to store information. You'll use your math skills to represent a fraction as a decimal to be stored in a variable.
This is part 1 of a 4-part series on coding. Click below to open the other tutorials in the series.
- Bee A Coder Part 2: Condition Statements
- Bee A Coder Part 3: If Statements
- Bee A Coder Part 4: Repeat Loops
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Learn to identify a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator using fraction models in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Educational Game
Test your fraction skills by answering questions on this site. This quiz asks you to simplify fractions, convert fractions to decimals and percentages, and answer algebra questions involving fractions. You can even choose difficulty level, question types, and time limit.
Type: Educational Game
Problem-Solving Tasks
The purpose of this task is to help students see the connection between a÷b and a/b in a particular concrete example. This task is probably best suited for instruction or formative assessment.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to help students gain a better understanding of fractions and the conversion of fractions into smaller units.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
The purpose of this task is to help students see the connection between a÷b and a/b in a particular concrete example. This task is probably best suited for instruction or formative assessment.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to help students gain a better understanding of fractions and the conversion of fractions into smaller units.
Type: Problem-Solving Task