General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Items may not contain fraction or decimal dimensions or volumes. Items may contain no more than two non-overlapping prisms – non-overlapping means that two prisms may share a face, but they do not share the same volume.
Items assessing MAFS.5.MD.3.5b may not contain the use or graphic of unit cubes.
Items assessing MAFS.5.MD.3.5c must contain a graphic of the figures.
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (3)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
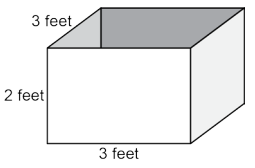
| Sample Item 1 | A shipping box in the shape of a rectangular prism has the dimensions shown.
V = l × w × h What is the volume, in cubic feet, of the box? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 2 | Select all the options that could be the dimensions of a rectangular prism with a
volume of 384 cubic feet (ft).
|
N/A | MS: Multiselect |
| Sample Item 3 | For MAFS.5.MD.3.5b: A right rectangular prism has a volume of 144 cubic centimeters and a height of 4 centimeters. What are a possible length and width, in centimeters, of the prism? V = l × w × h |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 5012070: | Grade Five Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7712060: | Access Mathematics Grade 5 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5020120: | STEM Lab Grade 5 (Specifically in versions: 2016 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012065: | Grade 4 Accelerated Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012015: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 3-5 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Volume Two Ways | Students are asked to compare different strategies for finding the volume of a rectangular prism. |
| Using Additive Reasoning When Finding Volume | Students are asked to find the volumes of solids composed of rectangular prisms. |
| Determining Dimensions | Students are given the total volume of a rectangular prism and constraints on one dimension and asked to provide dimensions that would fit the constraints. |
| Determining and Interpreting Volume | Students are asked to determine the volumes of two right rectangular prisms given the dimensions of one and the base area and height of the other. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| States of Matter and Their Properties - Mass and Volume Lesson #2 | When matter changes state, its properties change, too. In most cases, volume will increase when matter is melted from a solid to a liquid. Water is an exception, as its volume decreases when melted from ice to water. If matter is not added or removed, its mass will remain the same when it changes state. In this lesson, students will use if/then logical thinking to bridge the science and computer science concepts. This is lesson 2 of 3 in the States of Matter Unit. |
| Survive or Die | In this technology-rich lesson, students will design a habitat in which a plant or animal can survive. Students will focus on the adaptations that allow certain plants and animals to live in specific habitats. |
| Building Apartments: Connecting Volume of Centimeter Cubes to the Formula V = B x h | Students will build "apartments" with centimeter cubes by packing boxes (template included). In addition, they will use centimeter cubes to build a variety of rectangular prisms and record the area of the base (B) and height (h) on a worksheet. They will use that information to complete the volume formula, V = B x h. Students will think about how the volume changes as the height and base of rectangular prisms change. |
| Lunchbox Volume | This lesson focuses on the application of volume knowledge. Students will need to add the volumes of individual right rectangular prisms to find total volumes. |
| Volumize Your Brain To Its Capacity | Students will be able to apply and understand the meaning of volume with shoe boxes and cereal boxes. |
| Bakery Boxes in the Mail | Students need to make decisions about the correct bakery box to send cookies through the mail to fill orders. Students need to consider the capacity, dimensions, and volume of the boxes in terms of how many cookies each box will hold. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| MEA Bait Shop Baffle | Students will first review rectangular prisms and the formula for finding the volume of rectangular prisms. After students have determined the volume of a given set of rectangular prisms (aquariums), the students will use that information to help Seymour Phish in determining which aquarium he should purchase for his minnows. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Volume: Let's Be Efficient | This lesson provides a hands-on approach to develop the formula for finding the volume of a right rectangular prism. Students will apply the formula. Students will determine the volume of figures composed of two right rectangular-prism solids. While students will decompose simple 3 D shapes into two rectangular prisms, this decomposition is not required in the standard. It is used here to help deepened student understanding. |
| Growing Needs with Economy Boom! | In this MEA, students will use problem-solving strategies to rank different parking garages based on given factors. Students will need to apply their knowledge of volume to find the total volume of each parking garage and correctly calculate these values. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Cereal Box Volume Varying Predicament | Students will review rectangular prisms and the formula for finding the volume of rectangular prisms. Once students have determined the volume of a number of rectangular prisms (cereal boxes), the students will use that information to help a fictitious company in determining which cereal box they should use for their new product. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Building Pools | In this open-ended problem, students will work in teams to determine a procedure for ranking pools to help a customer purchase. Students will need to calculate the size and volume of the pool, make decisions based on a table of data, and write a letter to the customer providing evidence for their decisions. Students will need to tradeoff between the size of the pool, the customer service ranking, the type of pool and the warranty of the pool. The students will have to research on the internet the differences and benefits of a salt water pool versus a chlorinated one. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Building Rectangular Prisms Part 2 | This is the second part of a two-part volume lesson. In the first Building Rectangular Prisms (attached) lesson, foundational volume concepts are taught and students count cubes to find volume. In this lesson, students will discover the volume formulas length x width x height and base x height as they build rectangular prisms. They will use the formulas to find volume in real world situations. |
| Shoe Closet MEA | In this open-ended problem, students will work in teams to determine a procedure for ranking shoe closets for a company to purchase. Students will need to calculate the cubic feet of space for the closet, make decisions based on a table of data, and write a letter to the client providing evidence for their decisions. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Finding Volume (Utah Education Network) | In this lesson students will learn how to calculate and compare volumes of rectangular prisms. |
| Formulating Volume | Students will use situational stories to help them apply the formulas V = l × w × h and V = B × h to find the volumes of right rectangular prisms with whole-number edge lengths. |
| Relating Surface Area and Volume | Students will recognize that while the surface area may change, the volume can remain the same. This lesson is enhanced through the multimedia CPALMS Perspectives Video, which introduces students to the relationship between surface area and volume. |
Model Eliciting Activity (MEA) STEM Lesson
| Name | Description |
| Pump Up the Volume | This is a lesson on volume relating specifically to using the formula V = B x h. |
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Video Game Store: Volume! | Help solve the problem of shipping video games and accessories to customers by calculating the volume of the containers needed in this interactive tutorial. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Computing Volume Progression 2 | Students are asked to find the volume of water in a tank that is 3/4 of the way full. |
| Computing Volume Progression 3 | Students are asked to find the height of a rectangular prism when given the length, width and volume. |
| Computing Volume Progression 4 | Students are asked to apply knowledge of volume of rectangular prisms to find the volume of an irregularly shaped object using the principle of displacement. |
| Surface Area and Volume | In this activity, students adjust the dimensions of either a rectangular or triangular prism and the surface area and volume are calculated for those dimensions. Students can also switch into compute mode where they are given a prism with certain dimensions and they must compute the surface area and volume. The application keeps score so students can track their progress. This application allows students to explore the surface area and volume of rectangular and triangular prisms and how changing dimensions affect these measurements. This activity also includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet. |
Teaching Idea
| Name | Description |
| Volume of Rectangular Prisms | This lesson is designed to introduce students to the concept of volume and how to find the volume of rectangular prisms. This lesson provides links to discussions and activities related to volume as well as suggested ways to integrate them into the lesson. Finally, the lesson provides links to follow-up lessons designed for use in succession with the current one. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Volume through Decomposition | This Khan Academy tutorial video illustrates how to find the volume of an irregular solid figure by dividing the figure into two rectangular prisms and finding the volume of each. Although the tutorial works from a drawing, individual volume cubes are not drawn so students must work from the formula. |
| Volume: Decomposing a Solid Figure Example | This Khan Academy tutorial video illustrates finding the volume of an irregular figure made up of unit cubes by separating the figure into two rectangular prisms and finding the volume of each part. |
Unit/Lesson Sequence
| Name | Description |
| Three Dimensional Shapes | In this interactive, self-guided unit on 3-dimensional shape, students (and teachers) explore 3-dimensional shapes, determine surface area and volume, derive Euler's formula, and investigate Platonic solids. Interactive quizzes and animations are included throughout, including a 15 question quiz for student completion. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Video Game Store: Volume!: | Help solve the problem of shipping video games and accessories to customers by calculating the volume of the containers needed in this interactive tutorial. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Computing Volume Progression 2: | Students are asked to find the volume of water in a tank that is 3/4 of the way full. |
| Computing Volume Progression 3: | Students are asked to find the height of a rectangular prism when given the length, width and volume. |
| Computing Volume Progression 4: | Students are asked to apply knowledge of volume of rectangular prisms to find the volume of an irregularly shaped object using the principle of displacement. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Volume through Decomposition: | This Khan Academy tutorial video illustrates how to find the volume of an irregular solid figure by dividing the figure into two rectangular prisms and finding the volume of each. Although the tutorial works from a drawing, individual volume cubes are not drawn so students must work from the formula. |
| Volume: Decomposing a Solid Figure Example: | This Khan Academy tutorial video illustrates finding the volume of an irregular figure made up of unit cubes by separating the figure into two rectangular prisms and finding the volume of each part. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Computing Volume Progression 2: | Students are asked to find the volume of water in a tank that is 3/4 of the way full. |
| Computing Volume Progression 3: | Students are asked to find the height of a rectangular prism when given the length, width and volume. |
| Computing Volume Progression 4: | Students are asked to apply knowledge of volume of rectangular prisms to find the volume of an irregularly shaped object using the principle of displacement. |