General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Measurement conversions are from larger units to smaller units. Calculations are limited to simple fractions or decimals. Operations may include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Item contexts are not limited to distances, intervals of time, and money.
No
Required
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Gretchen is baking pies. She needs How many sticks of butter does Gretchen need to make 4 pies? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 2 | Jing participates in a trivia contest. He completes each question each question in How long does it take for Jing to complete 10 questions?
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 5012060: | Mathematics - Grade Four (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7712050: | Access Mathematics Grade 4 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5020110: | STEM Lab Grade 4 (Specifically in versions: 2016 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012065: | Grade 4 Accelerated Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012015: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 3-5 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Remote Control Motorcycle | Students are asked to solve a multi-step word problem involving money and unit conversions. |
| Kesha and Juan | Students are asked to solve a multi-step word problem that requires converting metric length units. |
| Shopping List | Students are asked to convert units of measure given with fractions and decimals using linear models. |
| Piano Lessons | Students are asked to use a number line to answer elapsed time questions. |
Image/Photograph
| Name | Description |
| Clipart ETC: Clock Menu | This website has over 2,000 illustrations of analog clocks. There are clocks with a variety of numeral fonts, and plain faces showing all possible times in one-minute increments. There are also an assortment of antique clocks, pocket watches, pendulums, hour glasses, and the interior devices of time pieces. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Making Cents of Taxes Part 1 | In this lesson plan, students will apply addition and subtraction skills with decimal values and multiplication of whole numbers to explore how taxes may impact citizens’ daily lives. |
| Volunteering with the Mayor Part 2 | Volunteering is vital to keeping any community safe, inviting, and running smoothly! In this lesson, students will work together to plan a volunteer project they would like to see happen in their community; as well as, create a budget for their project. |
| Volunteering with the Mayor | The mayor wants to build a new park in town! Volunteer your time and help the mayor design an expense report with a given budget for the new park in this lesson. |
| Making Cents of Taxes Part 2 | In this lesson plan, students will apply addition and subtraction skills with decimal values while exploring how taxes may impact citizen’s daily lives. |
| Dune or Doom: The Effects of Wind Erosion on Sand Dunes | In this lesson, students will address the following real-world problem of sand dune erosion while integrating Engineering Design concepts: Florida’s coastline has been ravaged by winds from hurricanes, resulting in damage to sand dunes and oceanfront properties. Your mission is to design the most effective barrier that would limit the amount of sand displaced from our tall sand dunes and prevent further damage to oceanfront buildings. Your designs can help us save the sand dunes before they are blown away! |
| Building up Beaches | In this STEM build, students will use problem solving skills and teamwork to model an effective way of slowing down beach erosion caused by the ocean. Students also will practice sharing their results through PowerPoint presentations. |
| Friction: Friend or Foe? | In this lesson, students will learn how different variables (mass, friction, and force) affect the motion of an object. |
| Washed Away | In this Engineering Design Challenge lesson, students will create a model beach and use different materials to find a solution to slow down the erosion process. |
| "Amazing Race-Elapsed Time" | In this lesson, which focuses specifically on the elapsed time portion of the standard, students work in small groups in a "race" to solve real world problems involving time. |
| Slither Not in the Everglades! Python MEA | This MEA will ask students to work in teams to help their client, The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, to decide which Burmese python traps manufacturing company to buy traps from. The traps will be placed along the Florida Keys and the Everglades to help prevent the growth of invasive Burmese Python population. The students will implement their knowledge of how plants, animals, and humans impact the environment, use mathematical and analytical problem-solving strategies, and be able report their finding in an organized, descriptive manner. |
| Traveling to the Moon MEA | This MEA is designed to help students create a process for selecting a Space Shuttle to send to the moon given the particular criteria provided. Students will master the Science Standard SC.4.E.5.2: Describe the changes in the observable shape of the moon over the course of about a month . Students will also practice and reinforce the Math Standard MAFS.4.MD.1.2: Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals. Represent fractional quantities of distance and intervals of time using linear models. Students will also practice ELA Standard LAFS.4.W.2.4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Supermarket Sweep! | In this lesson, students will use a grocery store ad to select items for purchase, working within the constraint of making their purchases with a $50 gift card. After their initial plan, they have some emergency expenses that change the amount of the gift card unexpectedly, and they must alter their list and re-compute how much money would remain on their gift card after their planned purchases are made. |
| Lizard Lights | Students will use a real-world problem solving situation to determine the best types of light bulbs to maintain an appropriate environment for a captive lizard. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Money Managers! | The main problem that the students are going to solve in this MEA is how to determine the appropriate allowance for a family of five children. This activity will allow the students to take on the role of financial planners as they examine a budget that has been earmarked by "The Davidson Family." The client has a particular amount of money to spare for their five children, however are unable to determine how much money each child should receive. The factors that students will need to consider at first will be the age of the children, the chores completed, and extracurricular activities the children engage in after school. The students might need to reconsider their thinking processes in order to take into account behavior comments and concerns that are also included. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Which Bank is Consumer Friendly? | This MEA is a student's exploration of banking. In the first task, they will create a model that will rank banks from most consumer friendly to least consumer friendly. In the second task, they will need to modify their models to address additional banks and additional criteria. Students can then test their models while researching real banks and determining their level of consumer friendliness. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Transportation Choices | In this MEA, students will determine which mode of transportation is best for a traveling sports team. They will have to decide between cost, time to travel, and comfort of travel. In the "twist," students are provided with more information including customer service rating of transportation as well as additional choices. Additionally, students will need to calculate the cost of the team's travel if they want the team to have a chance to win a drawing. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Tennis Lessons | This MEA asks students to take on the job of a tennis pro and decide which factors are most important in choosing a facility to take tennis lessons. Students will perform math calculations, create a two-column table for hours and minutes, develop a procedure to rank facilities, and provide written feedback through letters to a parent whose child needs group tennis lessons and writes letters to ask for advice. They will rank their choices from "best to worst" tennis lesson facilities. Students will provide a detailed written explanation for how they decided to rank factors and their solution for rating tennis lesson facilities. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Wondrous Water Parks | This activity requires students to apply their knowledge of unit conversions, speed calculation, and comparing fractions to solve the problem of which water park their class should choose to go on for their 5th grade class trip. |
| Pickle Pick | This Model Eliciting Activity (MEA) asks students to develop a procedure to select a pickle brand for a sandwich shop. Students will need to consider appearance, texture, price, flavor, length of shelf life, and estimating shipping costs. In the second portion of the problem statement, the students will need to trade off what they have previously considered and give more worth to the estimated shipping costs, while adding three more brands for consideration. The students will complete a culminating activity of making a commercial to advertise their selected brand. Student will need to work together and use the standard conventions of writing to write and perform their commercial for the other groups. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Plant Package | The Plant Package MEA provides students with an engineering problem in which they are asked to rank different plant containers using recycled materials. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Cookies and Treats | Fourth graders will help Cookies and Treats find cost-effective and eco-friendly packaging for its cookies. Students will organize data and compare prices using decimal notation in order to develop a procedure for choosing packaging for cookies. Students will use multiplication and division of whole numbers to plan for how many packages to order. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Banana County Public School-Painters MEA | This Model Eliciting Activity (MEA) is written at a 4th grade level. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Lotsa Lotion Lab's Sunscreens | Lotsa Lotion Labs requests the help of your team to rank a group of sunscreens, explain the process and justify how you chose which is 'best.' An additional hands-on lesson investigating solar energy and sunscreens is included as an extension activity. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| On the Hunt for Measurements: Estimation, Area and Perimeter of Rectangles | Students look for rectangular objects in the classroom or on the school campus that match the measurements for given clues. Students will estimate the measurements of the object, then take the exact measurements and use this information to determine its area and perimeter. |
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Making Cents of Taxes | Learn about sales tax as Malik tries to buy his favorite candy from the store in this short video. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Money in the piggy bank | This task is designed to help students focus on the whole that a fraction refers. It provides a context where there are two natural ways to view the coins. While the intent is to deepen a student's understanding of fractions, it does go outside the requirements of the standard. |
| Carnival Tickets | The purpose of this task is for students to solve multi-step problems in a context involving a concept that supports financial literacy, namely inflation. Inflation is a sustained increase in the average price level. In this task, students can see that if the price level increases and people’s incomes do not increase, they aren’t able to purchase as many goods and services; in other words, their purchasing power decreases. |
| What is 23 ÷ 5? | When a division problem involving whole numbers does not result in a whole number quotient, it is important for students to be able to decide whether the context requires the result to be reported as a whole number with remainder (as with Part (b)) or a mixed number/decimal (as with Part (c)). Part (a) presents two variations on a context that require these two different responses to highlight the distinction between them. |
Teaching Idea
| Name | Description |
| Ball Bounce Experiment | Students investigate different balls' abilities to bounce and represent the data they collect graphically. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Units of Measurement Word Problem: Making Change | This Khan Academy tutorial video presents a strategy for computing the amount of change to be received after making a purchase. |
| Time Word Problem: When to Leave to Get Home on Time | In this Khan Academy tutorial video Chris is told to be home by 6:15. You know the number of minutes it takes him to get home. What time should he leave? |
| How to convert gallons to quarts, quarts to pints, pints to cups, and cups to ounces | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore converting between gallons, quarts, pints, cups, and fluid ounces. |
| How to convert hours to minutes and minutes to seconds | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore conversion of units of time between hours, minutes and seconds. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Making Cents of Taxes: | Learn about sales tax as Malik tries to buy his favorite candy from the store in this short video. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Money in the piggy bank: | This task is designed to help students focus on the whole that a fraction refers. It provides a context where there are two natural ways to view the coins. While the intent is to deepen a student's understanding of fractions, it does go outside the requirements of the standard. |
| Carnival Tickets: | The purpose of this task is for students to solve multi-step problems in a context involving a concept that supports financial literacy, namely inflation. Inflation is a sustained increase in the average price level. In this task, students can see that if the price level increases and people’s incomes do not increase, they aren’t able to purchase as many goods and services; in other words, their purchasing power decreases. |
| What is 23 ÷ 5?: | When a division problem involving whole numbers does not result in a whole number quotient, it is important for students to be able to decide whether the context requires the result to be reported as a whole number with remainder (as with Part (b)) or a mixed number/decimal (as with Part (c)). Part (a) presents two variations on a context that require these two different responses to highlight the distinction between them. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Units of Measurement Word Problem: Making Change: | This Khan Academy tutorial video presents a strategy for computing the amount of change to be received after making a purchase. |
| Time Word Problem: When to Leave to Get Home on Time: | In this Khan Academy tutorial video Chris is told to be home by 6:15. You know the number of minutes it takes him to get home. What time should he leave? |
| How to convert gallons to quarts, quarts to pints, pints to cups, and cups to ounces: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore converting between gallons, quarts, pints, cups, and fluid ounces. |
| How to convert hours to minutes and minutes to seconds: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore conversion of units of time between hours, minutes and seconds. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Money in the piggy bank: | This task is designed to help students focus on the whole that a fraction refers. It provides a context where there are two natural ways to view the coins. While the intent is to deepen a student's understanding of fractions, it does go outside the requirements of the standard. |
| Carnival Tickets: | The purpose of this task is for students to solve multi-step problems in a context involving a concept that supports financial literacy, namely inflation. Inflation is a sustained increase in the average price level. In this task, students can see that if the price level increases and people’s incomes do not increase, they aren’t able to purchase as many goods and services; in other words, their purchasing power decreases. |
| What is 23 ÷ 5?: | When a division problem involving whole numbers does not result in a whole number quotient, it is important for students to be able to decide whether the context requires the result to be reported as a whole number with remainder (as with Part (b)) or a mixed number/decimal (as with Part (c)). Part (a) presents two variations on a context that require these two different responses to highlight the distinction between them. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| How to convert gallons to quarts, quarts to pints, pints to cups, and cups to ounces: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore converting between gallons, quarts, pints, cups, and fluid ounces. |
| How to convert hours to minutes and minutes to seconds: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, explore conversion of units of time between hours, minutes and seconds. |

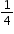 cup of butter for each pie. One stick of butter is
cup of butter for each pie. One stick of butter is 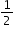 cup.
cup.