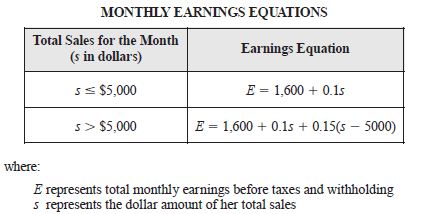General Information
Test Item Specifications
- In Lesson 1 students use mathematical models (tables and equations) to represent the relationship between the number of revolutions made by a "driver" and a "follower" (two connected gears in a system), and they will explain the significance of the radii of the gears in regard to this relationship.
- In Lesson 2 students mathematically model the growth of populations and use exponential functions to represent that growth.
Students will interpret and/or solve real-world problems involving linear equations or linear inequalities.
Items may require students to express inequalities on a number line, or to use an inequality for a response.
Items may include compound inequalities presented in written format, graphically, and/or algebraically.
Items will not include the use of interval notation, e.g. (3,∞), or set notation, e.g. { x I x > 3}.
Items must be set in real-world contexts.
Items should use methods that are graphical and/or algebraic.
Graphics should be used in some of these items, as appropriate.
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
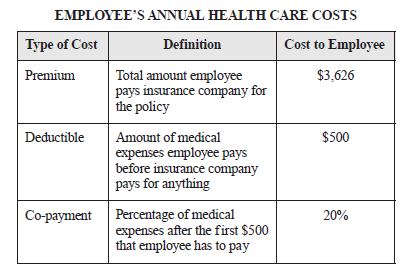
| Sample Item 1 | The out-of-pocket costs to an employee for health insurance and medical expenses for one year are shown in the table below. According to the plan outlined in the table, total annual health care costs, C, depend on the employee’s medical expenses for that year. If x represents the total medical expenses of an employee on this plan and x 500, which of the following equations can be used to determine this employee’s total health care costs for that year? |
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 2 | Karen works as a salesperson for a local marketing company. Using the equations shown below, the company calculates her monthly earnings based upon her total sales for the month. Karen’s total sales were greater than $5,000 in October. If her total monthly earnings for October were $3,000, what was the value of her total monthly sales, s ? |
N/A | FR: Fill-in Response |
Related Resources
Lesson Plan
| Name | Description |
| Math in Mishaps | Students will explore how percentages, proportions, and solving for unknowns are used in important jobs. This interactive activity will open their minds and address the question, "When is this ever used in real life?" |
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| MIT BLOSSOMS - The Broken Stick Experiment: Triangles, Random Numbers and Probability | This learning video is designed to develop critical thinking in students by encouraging them to work from basic principals to solve a puzzling mathematics problem that contains uncertainty. One class session of approximately 55 minutes is necessary for lesson completion. First-year simple algebra is all that is required for the lesson, and any high school student in a college-preparatory math class should be able to participate in this exercise. Materials for in-class activities include: a yard stick, a meter stick or a straight branch of a tree; a saw or equivalent to cut the stick; and a blackboard or equivalent. In this video lesson, during in-class sessions between video segments, students will learn among other things: 1) how to generate random numbers; 2) how to deal with probability; and 3) how to construct and draw portions of the X-Y plane that satisfy linear inequalities. |
Professional Development
| Name | Description |
| Mathematical Modeling: Insights into Algebra, Teaching for Learning | This professional development resource provides a rich collection of information to help teachers engage students more effectively in mathematical modeling. It features videos of two complete lessons with commentary, background information on effective teaching, modeling, and lesson study, full lesson plans to teach both example lessons, examples of student work from the lessons, tips for effective teaching strategies, and list of helpful resources. |
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Basic Linear Function | This video demonstrates writing a function that represents a real-life scenario. |
Worksheet
| Name | Description |
| Physics of Jumping-SeaWorld Classroom Activity | Students will determine jumping heights for various animals using a kinematic equation. |
Student Resources
Video/Audio/Animation
| Name | Description |
| Basic Linear Function: | This video demonstrates writing a function that represents a real-life scenario. |